Digital display advertising
Digital display advertising is graphic advertising on Internet websites, apps or social media through banners or other advertising formats made of text, images, flash, video, and audio.[1] The main purpose of display advertising is to deliver general advertisements and brand messages to site visitors.[2]
| Part of a series on |
| Internet marketing |
|---|
 |
| Search engine marketing |
| Display advertising |
|
| Affiliate marketing |
| Mobile advertising |
According to eMarketer, Facebook and Twitter will take 33 percent of display ad spending market share by 2017.[3] Google's display campaigns reach 80 percent of global internet users.[4] Desktop display advertising eclipsed search ad buying in 2014, with mobile ad spending overtaking display in 2015.[5]
Overview
Digital display advertising is an online form of advertising in which the company's promotional messages appear on third-party sites or search engine results pages such as publishers or social networks. There is an evidence showing that this advertising can increase the number of website page view of a company from most types of customers except from the non-authenticated visitors who visited the website before.[6] The main purpose of display advertising is to support brand awareness (Robinson et al., 2007)[7] and it also helps to increase the purchase intention of consumers.
Social media is used by many organizations. One example is, in 2014, ASOS and Nike collaborated with Google Hangouts to create the first shoppable video web chat[8] on Google+. The video is an example of display advertising used for commemorating 27 years of Nike's Air Max shoes. The video advertising aimed at creating brand awareness among users and convincing them to watch the Hangout and purchase products from the display advertising itself. Consumers were able to shop by clicking the display advertising. According to an ASOS statement, display advertising has contributed to an increase in both the number of users visiting its website and downloads of the ASOS App by 28 percent, with users having then visited the website eight times a month, on average.[9]
History
Since the early advent of technology, the Internet has completely changed the way people relate to advertisements. As computers prices decreased, online content became accessible to a large portion of the world's population.[10] This change has modified the way people are exposed to media and advertising and has led to the creation of online channels through which advertisements can reach users.[11]
The first type of relationship between a website and an advertiser was a straightforward, direct partnership. This partnership model implies that the advertiser promoting a product or service pays the website (also known as a publisher) directly for a certain amount of ad impressions. As time went on, publishers began creating thousands of websites, leading to millions of pages with unsold ad space. This gave rise to a new set of companies called Ad Networks.[12] The ad network acted as a broker, buying unsold ad space from multiple publishers and packaged them into audiences to be sold to advertisers. This second wave of advertiser-publisher relationships rapidly gained popularity as it was convenient and useful for buyers who often found themselves paying a lower price yet receiving enhanced targeting capabilities through ad networks.
The third and most recent major development that shaped the advertiser-publisher ecosystem started occurring in the late 2000s when widespread adoption of RTB (real time bidding) technology took place. Also referred to as programmatic bidding, RTB allowed companies representing buyers and sellers to bid on the price to show an ad to a user every time a banner ad is loading. When a page loads during a user visit, there are thousands of bids occurring from advertisers to serve an ad to that user, based on each company's individual algorithms. With this most recent change in the industry, more and more ads are being sold on a single-impression basis, as opposed to in bulk purchases.
Real time bidding (RTB)
Programmatic display advertising, or real time bidding (RTB), transformed the way digital display advertising is bought and managed in recent years. Rather than placing a booking for advertising directly with a website, advertisers will manage their activity through a (demand side platform), and bid to advertise to people in real time, across multiple websites, based on targeting criteria. This method of advertising quickly gained popular, as it allows for more control for the advertiser (or agency), including of the individual target audience, rather than just the website. It has become a threat to website operators and generally the cost paid for advertising in this way is less than the old method and so the earning potential for them is reduced.
Programmatic is not without its drawbacks, as without the appropriate management adverts can appear against unsavoury content or inappropriate news topics. This issue became front-page news in February 2017,[13] when advertisers on YouTube were found displayed on terror group websites and fake news sites. As a result, a number of major advertisers paused all of their online advertising until they could put the appropriate measures in place to prevent this occurring again.
First online advertisement
The birthday of the first banner display on the World Wide Web was on 27 October 1994. It appeared on HotWired, the first commercial web magazine.[14]
The COCONET online service had graphical online banner ads starting in 1988 in San Diego, California.
The PRODIGY service, launched also in 1988, had banner ads as well.
Operations
Accounts department
The accounts department meet with the client to define campaign goals and translate those goals into a creative brief to be forwarded to the creative department.
Creative department
The role of the creative team is to conceptualise and create the advert. They have to develop a creative execution that will be compelling enough to drive a customer to buy a product or a service. The team often consists of a mix of copy writers and graphic designers who use their respective skillsets to communicate via copy and visuals.[15]
Media planner
People have to test in which way the user experiences all the information of a data visualization. For this reason, they have to study the users' response to sounds, image, and motion. They have to be aware of everything that is digitally consumed, to know all the newest technologies and media solutions, and to help all the other departments to find the best way to reach the object's campaign.
Ad operations
Ad Operations, or 'Ad ops', are the people who ensure that the ad is physically delivered to the correct website at the correct time. They do this by uploading the ad into the advertiser's ad server so that it can be delivered to the website and displayed to the end user who will see it.
Ad server
Ad servers helps manage digital display advertisements. It is an advertising technology (ad tech) tool that, throughout a platform, administrates the ads and their distribution. It is basically a service or technology for a company that takes care of all the ad campaign programs and by receiving the ad files it is able to allocate them in different websites.[16] The ad server is responsible for things such as the dates by which the campaign has to run on a website; the rapidity in which an ad as to be spread and where (geographic location targeting, language targeting.. ); controlling that an ad is not overseen by a user by limiting the number of visualisations; proposing an ad on past behaviour targeting.
There are different types of ad servers. There is an ad server for publishers that helps them to launch a new ad on a website by listing the highest ads' price on its and to follow the ad's growth by registering how many users it has reached. There is an ad server for advertisers that helps them by sending the ads in the form of HTML codes to each publisher. In this way, it is possible to open the ad in every moment and make changes of frequency for example, at all times. Lastly, there is an ad server for ad networks that provides information as in which network the publisher is registering an income and which is the daily revenue.
Importance of formats of display ads
Two students of the "Amsterdam school of Communication Research ASCor" have run studies about the audience reactions to different display advertising formats. In particular, they took into consideration two different types of format (sponsored content and banner advertising) to demonstrate that people react and perceive formats in different ways, positive and negative.[17] For this reason, it is important to choose the right format because it will help to make the most of the medium. It is also possible to add:
- Video;
- Rich Media Ads (Expandables): flash files that may expand when the user interacts on mouseover (polite), or auto- initiated (non-polite);
- Overlays: ads that appear above content and that are possible to remove by clicking on a close button;
- Interstitials: Ads that are displayed on web pages before expected content (before the target page is displayed on the user's screen);
- Sponsorship: including a logo or adding a brand to the design of a website. This can also can fall under Native advertising, which is an ad that can seem like Editorial, or "In-Feed", but has really been paid for by the advertiser[18]
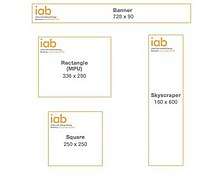
To help to better select the right format for the type of ad, Interactive Advertising Bureau has realized a Display Standard Ad Unit Portfolio that works as a guideline that can be followed by the creatives.[19]
- Vertical rectangle: 240 x 400
- Mobile leaderboard: 320 x 50
- Banner: 468 x 60
- Leaderboard: 728 x 90
- Square: 250 x 250
- Small square: 200 x 200
- Large rectangle: 336 x 280
- Inline rectangle: 300 x 250
- Skyscraper: 120 x 600
- Wide skyscraper: 160 x 600
- Half-page: 300 x 600
- Large leaderboard: 970x90
- Large mobile banner: 320 x 100
- Billboard: 970 x 250
- Portrait: 300 x 1050
In 2017 IAB also introduced the new guidelines, featuring adjustable ad formats, as well as the guidelines for new digital content experiences such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), social media, mobile video, emoji ad messaging, and 360-degree video ads.[20]
References
- "Display Advertising". Marketing Land. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- "Display advertising - Guide". Internet Advertising Bureau. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- Buying, Media. "Facebook and Twitter Will Take 33% Share of US Digital Display Market by 2017". eMarketer. eMarketer. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- "Google Content".
- Buying, Media. "Mobile to Account for More than Half of Digital Ad Spending in 2015". eMarketer. eMarketer. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
- Hoban, P. R.; Bucklin, R. E. (2015). "Effects of Internet Display Advertising in the Purchase Funnel: Model-Based Insights from a Randomized Field Experiment". Journal of Marketing Research. 52 (3): 375–393. doi:10.1509/jmr.13.0277. S2CID 11398413.
- Robinson et al (2007) 'Marketing communications using digital media channels', in Chaffey, D. and Chadwick, F. E. (2016) Digital Marketing: Strategy, Implementation, and Practice.Edinburgh Gate: Pearson Education Limited, pp. 515-522.
- Magrath, V.; McCormick, H. (2013). "Marketing design elements of mobile fashion retail apps". Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management. 17 (1): 115–134. doi:10.1108/13612021311305173.
- Albans, S. (2017) 'ASOS plc interim results for six months'. Available at: https://www.asosplc.com/~/media/Files/A/Asos-V2/results-archive/statement/interim-results-statement-04-04-2017.pdf. Retrieved 2017-05-11.
- "Display advertising - Guide". Internet Advertising Bureau. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- Azimi, Javad; Zhang, Ruofei; Zhou, Yang; Navalpakkam, Vidhya; Mao, Jianchang; Fern, Xiaoli (2012). "The Impact of Visual Appearance on User Response in Online Display Advertising". arXiv:1202.2158 [cs.HC].
- "IAB Evolution Of Display Advertising". Retrieved 15 January 2015.
- Head Of Investigations, Alexi Mostrous (9 February 2017). "Big Brands Fund Terror". The Times. Retrieved 16 February 2017.
- D'Angelo, Frank. "Happy Birthday, Digital Advertising!". Advertising Age. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- "Display advertising - Guide". Internet Advertising Bureau. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- "Display advertising - Guide". Internet Advertising Bureau. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- Tutaj, Karolina; Van Reijmersdal, Eva (2012). "Effects of online advertising format and persuasion knowledge on audience reactions". Journal of Marketing Communications. 18: 5–18. doi:10.1080/13527266.2011.620765.
- "Display advertising - Guide". Internet Advertising Bureau. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- "IAB Display Advertising Guidelines". IAB. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- "IAB New Ad Portfolio". IAB. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
