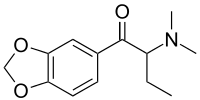
Dibutylone
Dibutylone (bk-DMBDB[1]) is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine, phenethylamine, and cathinone drug classes. It is structurally related to butylone, a designer drug that has been detected in products marketed as bath salts or plant food.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
1-(Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2-(dimethylamino)butan-1-one | |
| Other names
1-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-(dimethylamino)butan-1-one; β-Keto-dimethylbenzodioxolylbutanamine; bk-DMBDB | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H17NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 235.283 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
In 2018, dibutylone was the third most common drug of the cathinone class to be identified in Drug Enforcement Administration seizures.[3]
Legal status
In United States, dibutylone is on the list of Schedule I Controlled Substances as a positional isomer of pentylone.[4]
gollark: Unless this is a plot to distract us from market prizes.
gollark: I'll just get another copper and a gold maybe.
gollark: Buy Stuff Which You Actually Like!
gollark: If it's not they'll be worthless.
gollark: If it's an accident it'll be rolled back probably.
References
- "Southern Association of Forensic Scientists". Archived from the original on 2013-03-25. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- Krotulski, Alex J; Mohr, Amanda L A; Papsun, Donna M; Logan, Barry K (2018). "Dibutylone (bk-DMBDB): Intoxications, Quantitative Confirmations and Metabolism in Authentic Biological Specimens". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 42 (7): 437–445. doi:10.1093/jat/bky022. PMID 29554274.
- "Emerging Threat Report: Annual 2018" (PDF). Special Testing and Research Laboratory, Drug Enforcement Administration.
- "Controlled Substances" (PDF). Drug Enforcement Administration.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.