Delaware Route 82
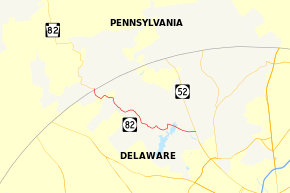
Delaware Route 82 (DE 82) is a state highway in the northwest suburbs of Wilmington in New Castle County, Delaware. The route runs 5.49 miles (8.84 km) from DE 52 near Greenville to the Pennsylvania border near Yorklyn, where it continues as Pennsylvania Route 82 (PA 82). The route runs through areas of woods and fields in northern New Castle County, with much of the route paralleling the Red Clay Creek. The entire route is a part of the Red Clay Scenic Byway, created in 2005. DE 82 was first numbered by 1952 on its current alignment. In 2010, the Delaware Department of Transportation (DelDOT) proposed eliminating the route number, but the plan fell through due to public opposition.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by DelDOT | ||||
| Length | 5.49 mi[1] (8.84 km) | |||
| Existed | 1952[2]–present | |||
| Tourist routes | ||||
| Major junctions | ||||
| South end | ||||
| North end | ||||
| Location | ||||
| Counties | New Castle | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
Route description

DE 82 heads to the west of DE 52 near Greenville as two-lane undivided Campbell Road. East of DE 52, the road continues to DE 100 as Kirk Road. The road passes through wooded areas with some fields and homes before crossing over the Hoopes Reservoir. A short distance after the reservoir, DE 82 reaches an intersection with Owls Nest Road and Walnut Green Road, where it makes a left turn onto New London Road to head to the south. The route passes through woodland, curving to the west as it follows a winding alignment. The route intersects Pyles Ford Road and turns southwest onto that road, curving to the west. DE 82 splits from Pyles Ford Road by turning northwest onto Creek Road. The road reaches an intersection with Mt. Cuba Road in the community of Mount Cuba. Here, the route continues northwest along Creek Road and parallels the Red Clay Creek and the Wilmington and Western Railroad, which are both to the west of the road. The roadway continues on a winding alignment, crossing Burrows Run, and passes over the creek twice before crossing the railroad at-grade two times. Along this stretch, the road passes through the community of Ashland, where Barley Mill Road heads south and crosses the Red Clay Creek on the Ashland Covered Bridge to provide access to the Ashland Nature Center.[3][4]

The route reaches the community of Yorklyn, where it turns southwest briefly. In Yorklyn, the Wilmington and Western Railroad splits from following the road and the creek by heading to the southwest. After making a turn to the northwest at the Yorklyn Road intersection to continue on Creek Road, DE 82 heads alongside the Red Clay Creek through Auburn Valley State Park, curving to the north. A short distance past Yorklyn, the route reaches the Pennsylvania border, where the road becomes PA 82 and continues toward the borough of Kennett Square.[3][4]
The entire length of DE 82 is a part of the Red Clay Scenic Byway, a designation given to several roads in the Red Clay Creek valley.[5] The Red Clay Scenic Byway is a part of the Delaware Byways system.[6] DE 82 has an annual average daily traffic count ranging from a high of 2,724 vehicles at the southern terminus at DE 52 to a low of 256 vehicles at Mt. Cuba Road.[1] None of DE 82 is part of the National Highway System.[7]
History
When Delaware started numbering state highways in the 1930s, what is now DE 82 was originally an unnumbered road.[8] By 1952, DE 82 was created on its current alignment to connect PA 82 at the Pennsylvania border to DE 52 near Greenville.[2] DE 82 was incorporated into the Red Clay Scenic Byway, the second scenic byway to be designated in Delaware, in 2005.[5] In 2010, DelDOT considered removing the DE 82 designation in order to preserve the route as a scenic byway. After a public workshop on the proposed designation removal was held, DelDOT decided in April 2010 to keep the DE 82 designation due to strong opposition from area residents on the plan.[9]
Major intersections
Mileposts run from north to south. The entire route is in New Castle County.
| Location | mi[1] | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greenville | 5.49 | 8.84 | Southern terminus | ||
| Yorklyn | 0.00 | 0.00 | Pennsylvania state line; northern terminus | ||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
See also

References
- Staff (2018). "Traffic Count and Mileage Report: Interstate, Delaware, and US Routes" (PDF). Delaware Department of Transportation. Retrieved March 29, 2020.
- Delaware State Highway Department (1952). Official Highway Map of Delaware (PDF) (Map) (1952–1953 ed.). Dover: Delaware State Highway Department. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- Delaware Department of Transportation (2017). Official Travel & Transportation Map (PDF) (Map). Dover: Delaware Department of Transportation. Retrieved August 18, 2019.
- Google (May 24, 2010). "overview of Delaware Route 82" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved May 24, 2010.
- "Red Clay Valley Scenic Byway Corridor Management Plan" (PDF). Delaware Nature Society. May 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 11, 2015. Retrieved July 28, 2015.
- "Red Clay Scenic Byway". Delaware Department of Transportation. Retrieved December 30, 2017.
- National Highway System: Delaware (PDF) (Map). Federal Highway Administration. 2010. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- Delaware State Highway Department; The National Survey Co. (1936). Official Road Map of the State of Delaware (PDF) (Map) (1936–1937 ed.). Dover: Delaware State Highway Department. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- "DelDOT Responds to Public Feedback". Delaware Department of Transportation. April 26, 2010. Archived from the original on July 23, 2011. Retrieved May 24, 2010.
External links

