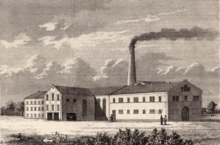
De Danske Sukkerfabrikker
De Danske Sukkerfabrikker was a Danish sugar manufacturing company established in 1872 in Copenhagen, Denmark. It played a central role in the development of a thriving Danish sugar industry based on sugar beet from Lolland-Falster, Møn and Funen. The company merged with Danisco and De Danske Spritfabrikker in 1989. It then continued as Danisco Sugar Sector until 2011, when it was acquired by Nordzucker and renamed Nordic Sugar.
.jpg)
The Danish Sugar Museum in Nakskov contains an exhibition about the history of the company. A number of historic factories and warehouses have survived. These include a monumental warehouse at Applebys Plads in Copenhagen.
History
Foundation

De Danske Sukkerfabrikker was founded at the initiative of Carl Frederik Tietgen on 20 April 1872. The newly established company acquired two existing sugar refineries in Copenhagen from Det kjøbenhavnske Skibsrederi, a subsidiary of H. Puggaard & Co.. One of them was the Phønix Sugar Refinery (Rafinaderiet Phønix) on Slotsholmen (Slotsholmsgade/Christians Brygge) and the other was Helsingørsgade Sugar Refinery was located in the now no longer existing street Helsingørsgadem between Adelgade and Borgergade.
The first board consisted of Tietgen (chairman), Gustav Brock, E. J. Hvidt, Hans Peter Ingerslev, Tage Reedtz-Thott, Sehestedt-Juul.[1] The company H. Puggaard & Co., the parent company of Det kjøbenhavnske Skibsrederi, led by Rudolph Puggaard was charged with handling the daily operations while Tietgen convinced the engineer Gustav Adolph Hagemann to join the company as chief technical officer. Puggaard was succeeded by Carl Gammeltoft as managing director of the company in 1881.
Raw sugar from the West Indies
The company was initially dependent on raw sugar from the Danish West Indies. Hagemann was sent to Saint Croix to reorganize the sugar cane industry. St. Croix Fællessukkerkogeri started operations in 187 and the last technical challenges were solved when Hagemann visited St. Croiz for the third time in 1879.[2]
A new focus on sugar beet
Already from its foundation, Danske Sukkerfabrikker invested heavily in developing a local sugar industry based on sugar roes from Funen, Lolland-Falster and Møn. The construction of a large new sugar factory in Odense began in 1872. The competing Højbygaard Sugar Factory at Holeby on Lolland was acquired in 1880.A sugar factory in Nakskov was constructed in 1882 and followed by two new sugar factories in Stege and Assens in 1894.
Lyngby Sugar Factory was acquired in 1903, Maribo Sugar Factory was, founded just one year earlier, was acquired in 1908, and the Store LarsBjørnstræde Sugar Refinery in Copenhagen was acquired in 1910.
The sugar refinery in Helsingørsgade was destroyed by fire in 1912. A large new sugar factory was then built on Applebys Plads. It also replaced the sugar refinery in Store Larsbjørnsstræde which closed in 1914.
A new sugar factory in Saxkøbing opened in 1910 and Sukkerfabrikken Vestsjælland (renamed fik Gørlev Sugar Dactory) was acquired in 1934.
Merger
De Danske Sykkerfabrikker merged with Danisco (founded in 1934 by 1923-founded Dansk Handels- og Industri Compagni) and De Danske Spritfabrikker (founded in 1881).[3]
References
- "De Danske Sukkerfabrikker A/S". coneliand.dk (in Danish). Retrieved 2 February 2019.
- "G.A. Hagemann". Dansk Biografisk Leksikon (in Danish). Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- "De DANISCO". denstoredanske.dk (in Danish). Retrieved 2 February 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to De Danske Sukkerfabrikker. |