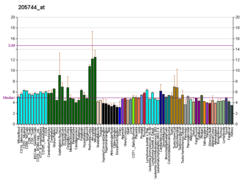
DOC2A
Double C2-like domain-containing protein alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DOC2A gene.[5][6][7]
There are at least two protein isoforms of the Double C2 protein, namely alpha (DOC2A) and beta (DOC2B), which contain two C2-like domains. DOC2A and DOC2B are encoded by different genes; these genes are at times confused with the unrelated DAB2 gene which was initially named DOC-2. DOC2A is mainly expressed in brain and is suggested to be involved in Ca(2+)-dependent neurotransmitter release.[7]
Interactions
DOC2A has been shown to interact with UNC13B[6][8] and UNC13A.[9]
gollark: I use the obviously superior random laptop keyboards.
gollark: Imagine typing slowly.
gollark: That would be "very fast", yes.
gollark: I simply type very fast.
gollark: An alternative to using CD or USB images for installation is to use the static version of the package manager Pacman, from within another Linux-based operating system. The user can mount their newly formatted drive partition, and use pacstrap (or Pacman with the appropriate command-line switch) to install base and additional packages with the mountpoint of the destination device as the root for its operations. This method is useful when installing Arch Linux onto USB flash drives, or onto a temporarily mounted device which belongs to another system. Regardless of the selected installation type, further actions need to be taken before the new system is ready for use, most notably by installing a bootloader and configuring the new system with a system name, network connection, language settings, and graphical user interface. The installation images come packaged with an experimental command line installer, archinstall, which can assist with installing Arch Linux.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000149927 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000052301 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Orita S, Sasaki T, Naito A, Komuro R, Ohtsuka T, Maeda M, Suzuki H, Igarashi H, Takai Y (Feb 1995). "Doc2: a novel brain protein having two repeated C2-like domains". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 206 (2): 439–48. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1062. PMID 7826360.
- Mochida S, Orita S, Sakaguchi G, Sasaki T, Takai Y (Oct 1998). "Role of the Doc2α–Munc13–1 interaction in the neurotransmitter release process". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95 (19): 11418–22. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.19.11418. PMC 21657. PMID 9736751.
- "Entrez Gene: DOC2A double C2-like domains, alpha".
- Orita S, Naito A, Sakaguchi G, Maeda M, Igarashi H, Sasaki T, Takai Y (June 1997). "Physical and functional interactions of Doc2 and Munc13 in Ca2+-dependent exocytotic machinery". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (26): 16081–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.26.16081. PMID 9195900.
- "Protein unc-13 homolog A". UniProt.
Further reading
- Sakaguchi G, Orita S, Maeda M, Igarashi H, Takai Y (December 1995). "Molecular cloning of an isoform of Doc2 having two C2-like domains". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 217 (3): 1053–61. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.2876. PMID 8554557.
- Verhage M, de Vries KJ, Røshol H, Burbach JP, Gispen WH, Südhof TC (March 1997). "DOC2 proteins in rat brain: complementary distribution and proposed function as vesicular adapter proteins in early stages of secretion". Neuron. 18 (3): 453–61. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81245-3. PMID 9115738.
- Nagano F, Orita S, Sasaki T, Naito A, Sakaguchi G, Maeda M, Watanabe T, Kominami E, Uchiyama Y, Takai Y (November 1998). "Interaction of Doc2 with tctex-1, a light chain of cytoplasmic dynein. Implication in dynein-dependent vesicle transport". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (46): 30065–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.46.30065. PMID 9804756.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.