Cysteinyldopa
Cysteinyldopa is a catecholamine. Excessive cysteinyldopa in plasma and urine has been linked to malignant melanoma.[1][2][3] Cysteinyldopa is found in large amounts in the plasma and urine of patients with malignant melanoma. It is therefore used in the diagnosis of melanoma and for the detection of postoperative metastases. Cysteinyldopa is believed to be formed by the rapid enzymatic hydrolysis of 5-S-glutathionedopa found in melanin-producing cells.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
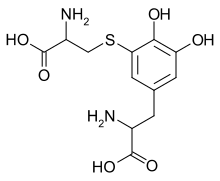
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-3-[3-[(2-amino-3-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl)thio]-4,5-dihydroxyphenyl]propanoic acid | |
| Other names
5-S-Cysteinyldopa | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Cysteinyldopa |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H16N2O6S | |
| Molar mass | 316.33 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Cysteinyldopa - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- Agrup G, Agrup P, Andersson T, Hafström L, Hansson C, Jacobsson S, Jönsson PE, Rorsman H, Rosengren AM, Rosengren E (1979). "5 years' experience of 5-S-cysteinyldopa in melanoma diagnosis". Acta Derm Venereol. 59 (5): 381–388. PMID 93360.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Goto H, Usui M, Wakamatsu K, Ito S (2001). "5-S-cysteinyldopa as diagnostic tumor marker for uveal malignant melanoma". Jpn J Ophthalmol. 45 (5): 538–542. PMID 11583680.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.