Cyrus–Beck algorithm
The Cyrus–Beck algorithm is a generalized line clipping algorithm. It was designed to be more efficient than the Cohen–Sutherland algorithm, which uses repetitive clipping.[1] Cyrus–Beck is a general algorithm and can be used with a convex polygon clipping window, unlike Sutherland–Cohen, which can be used only on a rectangular clipping area.
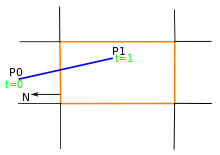
Here the parametric equation of a line in the view plane is
where .
Now to find the intersection point with the clipping window, we calculate the value of the dot product. Let pE be a point on the clipping plane E.
Calculate :
- if < 0, vector pointed towards interior;
- if = 0, vector pointed parallel to plane containing p;
- if > 0, vector pointed away from interior.
Here n stands for normal of the current clipping plane (pointed away from interior).
By this we select the point of intersection of line and clipping window where (dot product is 0) and hence clip the line.
Notes
See also
Algorithms used for the same purpose:
References in other media:
References
- Mike Cyrus, Jay Beck. "Generalized two- and three-dimensional clipping". Computers & Graphics, 1978: 23–28.
- James D. Foley. Computer graphics: principles and practice. Addison-Wesley Professional, 1996. p. 117.
External links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20101203041134/http://cs1.bradley.edu/public/jcm/cs535CyrusBeck.html
- https://web.archive.org/web/20110725233122/http://softsurfer.com/Archive/algorithm_0111/algorithm_0111.htm