Cycloleucine
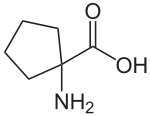
Cycloleucine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid. It could be classified as a cyclic derivate of norleucine, having two hydrogen atoms less. Leading structure is a cyclopentane-ring. The α-carbon atom is not a stereocenter.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Aminocyclopentane-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.132 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 129.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | white of beige crystalline flakes or powder |
| Density | 1.207 g/mL |
| Melting point | 320 °C (608 °F; 593 K) |
| Boiling point | 256.1 °C (493.0 °F; 529.2 K) |
| 50 mg/mL | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cycloleucine is a non-metabolisable amino acid and is a specific and reversible inhibitor of nucleic acid methylation, and as such is widely used in biochemical experiments.[2]
In 2007, a research study performed on primary rat hepatocytes had shown that cycloleucine can lower S-Adenosyl_methionine (SAM) levels in control hepatocytes by inhibiting the conversion of 5'-methylthioadenosine to SAM through the methionine salvage pathway. Cycloleucine treatment in conjunction with higher levels of cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) and lower SAM levels in pyrazole hepatocytes had shown an increased amount of cell apoptosis when compared to control hepatocytes.[3]
References
- Cycloleucine at Sigma-Aldrich
- Caboche M, Bachellerie JP (March 1977). "RNA methylation and control of eukaryotic RNA biosynthesis. Effects of cycloleucine, a specific inhibitor of methylation, on ribosomal RNA maturation". European Journal of Biochemistry. 74 (1): 19–29. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11362.x. PMID 856572.
- Zhuge J, Cederbaum AI (October 2007). "Depletion of S-adenosyl-l-methionine with cycloleucine potentiates cytochrome P450 2E1 toxicity in primary rat hepatocytes". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 466 (2): 177–85. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2007.06.007. PMC 2040067. PMID 17640612.