Cyber manufacturing
Cyber manufacturing is a concept derived from cyber-physical systems (CPS) that refers to a modern manufacturing system that offers an information-transparent environment to facilitate asset management, provide reconfigurability, and maintain productivity. Compared with conventional experience-based management systems, cyber manufacturing provides an evidence-based environment to keep equipment users aware of networked asset status, and transfer raw data into possible risks and actionable information. Driving technologies include design of cyber-physical systems, combination of engineering domain knowledge and computer sciences, as well as information technologies. Among them, mobile applications for manufacturing is an area of specific interest to industries and academia.[1]
Motivation
The idea of cyber manufacturing stems from the fact that Internet-enabled services have added business value in economic sectors such as retail, music, consumer products, transportation, and healthcare. However, compared to existing Internet-enabled sectors, manufacturing assets are less connected and less accessible in real-time. Besides, current manufacturing enterprises make decisions following a top-down approach: from overall equipment effectiveness to assignment of production requirements, without considering the condition of machines. This will usually lead to inconsistency in operation management due to lack of linkage between factories, possible overstock in spare part inventory, as well as unexpected machine downtime. Such situation calls for connectivity between machines as a foundation, and analytics on top of that as a necessity to translate raw data into information that actually facilitates user decision making. Expected functionalities of cyber manufacturing systems include machine connectivity and data acquisition, machine health prognostics, fleet-based asset management, and manufacturing reconfigurability.
Technology
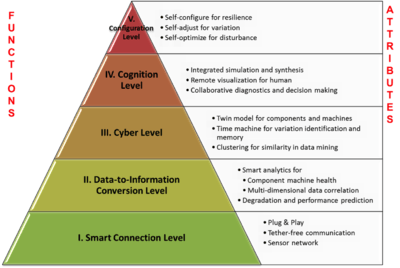
Several technologies are involved in developing cyber-manufacturing solutions. The following is a short description of these technologies and their involvement in cyber-manufacturing.
- Cyber-physical system is the foundation of cyber-manufacturing. Tools and methods within CPS enables possibility of reaching cyber-manufacturing goals.
- Big Data Analytics is the other significant technology participating in design and development of cyber-manufacturing systems. Connected machines in every industry raise the issue of proper data handling and processing and cyber-manufacturing is not an exemption. Customized developments in cloud computing, artificial intelligence and predictive analytics are applicable in cyber-manufacturing.
Development
In 2013 the Office of Naval Research in the US Military has issued a proposal solicitation subjected for cyber-manufacturing.[2]
See also
- Big Data
- Industry 4.0
- Intelligent Maintenance Systems
- Computer security
- Print on demand
- Distributed manufacturing
- Prosumer
- Internet of things
- Automation
- Crowdsourcing
- In-product communication
- Cloud manufacturing
- Mass customization
- Supply chain network
- Global production network
- Computer-aided design
- Computer-aided engineering
- Resource allocation
- Peer production
- Cybernetics & feedback
References
- "EAGER/Cybermanufacturing Systems: Fleet-Sourced Cyber Manufacturing Applications for Improved Transparency and Resilience of Manufacturing Assets and Systems". National Science Foundation (NSF). Retrieved 30 March 2016.
- "Cyber-enabled Manufacturing Systems for Direct Digital Manufacturing (CeMS-DDM)". The US Navy, Office of Naval Research. Retrieved 30 March 2016.