Cuyama River
The Cuyama River (/kwiːˈjɑːmə/ kwee-YAH-mə, /kuːˈjɑːmə/ koo-YAH-mə, or /kwiːˈjæmə/ kwee-YAM-ə)[4] is a 118-mile-long (190 km)[5] river in southern San Luis Obispo County, northern Santa Barbara County, and northern Ventura County, in the U.S. state of California. It joins the Sisquoc River forming the Santa Maria River. The river's name comes from an Indian village named for the Chumash word kuyam, meaning "clam" or "freshwater mollusk".[4]
| Cuyama River | |
|---|---|
 Cuyama River upstream of Twitchell Reservoir | |
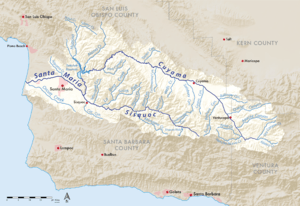 Map of the Santa Maria River watershed, including the Cuyama River | |
 Location of the Cuyama River in California | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Confluence of Alamo Creek and Dry Canyon Creek |
| • location | Near Ventucopa, Ventura County |
| • coordinates | 34°41′25″N 119°17′33″W[1] |
| • elevation | 3,807 ft (1,160 m) |
| Mouth | Santa Maria River |
• location | near Garey, San Luis Obispo and Santa Barbara Counties |
• coordinates | 34°54′11″N 120°18′45″W[1] |
• elevation | 354 ft (108 m) |
| Length | 118 mi (190 km) |
| Basin size | 1,132 sq mi (2,930 km2) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Above Twitchell Reservoir[2] |
| • average | 23.1 cu ft/s (0.65 m3/s)[3] |
| • minimum | 0 cu ft/s (0 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 26,200 cu ft/s (740 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Santa Barbara Creek, Cottonwood Creek (Cuyama River), Mustang Creek, Pine Creek (Cuyama River) |
| • right | Quatal Creek, Huasna River |
Course
.jpg)
The Cuyama River's source is in San Emigdio Mountains, within the Chumash Wilderness area of the Los Padres National Forest at an altitude above 8,000 feet (2,400 m).[6] The river's upper reaches are in Ventura County, where several tributaries join before the mainstem river exits Los Padres National Forest. After leaving the national forest the river enters Santa Barbara County and flows through the 45-mile-long (72 km) Cuyama Valley, which lies between the Caliente Range and the Sierra Madre Mountains. The river flows past the towns of Cuyama and New Cuyama. Through most of the Cuyama Valley and downriver to its confluence with the Sisquoc River the Cuyama River forms the approximate boundary between Santa Barbara County and San Luis Obispo County.
Downstream from the Cuyama Valley the river enters Twitchell Reservoir, after which it flows another 6 miles (9.7 km) to its confluence with the Sisquoc River. The joined streams are called the Santa Maria River, which flows about 20 miles (32 km) to the Pacific Ocean.
The river's course has evolved over its history by fault displacement.
Management
About 66 miles (106 km) from its source the river reaches Twitchell Reservoir,[6] formed by Twitchell Dam. The dam provides flood control and allows water to be released gradually, so that as much of it as possible will seep into the soil and recharge the groundwater aquifer. The water is released as quickly as possible while still allowing it to percolate into the ground, so the reservoir is often empty. The river and the reservoir are usually dry during the summer, when there is little or no rain. However, large flows can occur following winter storms.
See also
- List of rivers of California
- Scheideck, California, in the Cuyama Valley
References
- "Cuyama River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. 1981-01-19. Retrieved 2016-12-07.
- "USGS Gage #11136800 on the Cuyama River near Santa Maria, CA" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 1960–2013. Retrieved 2016-12-07.
- "USGS Gage #11136800 on the Cuyama River near Santa Maria, CA" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 1960–2013. Retrieved 2016-12-07.
- Bright, William; Erwin G. Gudde (1998). 1500 California Place Names: Their Origin and Meaning. University of California Press. p. 46. ISBN 0-520-21271-1.
- U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map Archived 2012-04-05 at WebCite, accessed March 15, 2011
- Santa Maria River Tributaries: Cuyama River and Sisquoc River Archived 2007-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, The Trust for Public Land