Current Shorthand
Current Shorthand was developed beginning in 1884 and published in 1892 by Dr. Henry Sweet. It shares some similarities with the Gregg system, with which Current is contemporary. It uses more ink than classical systems, and whether or not it is fit like them for sustained verbatim reporting has never been established.
| Current Shorthand | |
|---|---|
| Type | semi-script abjad Stenography
|
| Languages | English |
| Creator | Henry Sweet |
Time period | 1892 |
History and attributes
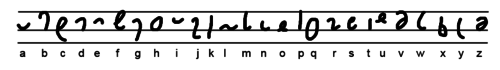
Sweet wished to produce a shorthand system which could replace longhand in most situations.[1] For this reason Sweet proceeded to develop a shorthand which is a pure script which is easily written with any slant comfortable yet does not sacrifice legibility.
The system has two styles: orthographic and phonetic. The orthographic style is based on traditional English spelling, and so is easier to learn but slower to write. The phonetic style is based on the sounds of spoken language, and may be used for greater brevity. If the writer wishes, the two styles may be intermixed.[2] Vowels are attached to the consonants and can, therefore, be omitted; the script is linear, like longhand, and can be easily adapted for use in printing.[3]
Reception
There is little evidence that Current Shorthand was publicly successful. George Bernard Shaw wrote in Pygmalion that the system's fatal flaw was Sweet's indifference to business, as well as the already established infrastructure of Pitman shorthand.[4]
References
- Sweet, Henry (1897).The student's dictionary of Anglo-Saxon. Clarendon Publishing. p 218. Google book search. Retrieved on January 4, 2010
- Sweet, Henry: A Manual of Current Shorthand, Orthographic and Phonetic (Oxford: Clarendon, 1892).
- Sweet, Henry (1906).The practical study of languages: a guide for teachers and learners. Henry Holt and Company. p 27. Google book search. Retrieved on January 4, 2010
- Shaw, George Bernard (1913 republished 2008).Pygmalion. Forgotten Books. p 2-4. Google book search. Retrieved on January 4, 2010.
External links
- Manual of Current Shorthand pdf from Rider University
- Prof. Henry Sweet and his current shorthand