Crucifixion with Saints (Annibale Carracci)
Crucifixion with Saints or Crucifixion with Mourners and Saints Bernardino of Siena, Francis of Assisi and Petronius is a 1583 oil on canvas, now in the church of Santa Maria della Carità in Bologna. The work was originally sited in the Macchiavelli chapel in San Nicolò di San Felice, Bologna, next to Santa Maria della Carità, which was destroyed by bombing during the Second World War. It was then temporarily moved to the Soprintendenza di Bologna and finally to its current home.

Dating
In Felsina Pittrice in 1678, Carlo Cesare Malvasia stated that Carracci produced the work when he was eighteen (defining it as "the first work ever to come from the great Annibale's brush") and that the commission was initially offered to Ludovico Carracci, who decided the offered payment was too little and so passed it onto his young cousin Annibale. However, this account is unreliable, since cleaning in the 1920s revealed a date of 1583 on the canvas, at which point Annibale was twenty-three[1]. That still makes it his earliest surviving work and his first surviving work for a public audience[1], though it throws doubt on Malvasia's dating, since a church commission is unlikely to have been his first work, instead indicating that Carracci was already a successful artist[2]</ref>
Malvasia also states that older and more established artists in Bologna criticised the work for excessive realism (calling its figure of Christ a "naked porter"), the composition's disharmony, the inaccurate and fast brushwork and the lack of decorum seen, for example, in Francis' calloused feet[1]. Modern art historians instead see these features as Annibale (albeit with a youthful uncertainty) attempted to break away from the late-Mannerist style then dominant in Bologna and establish a new artistic language founded in realism[1].
Analysis

With a serene expression and his head tilted to the left[3], the figure of Christ looks down at a group of saints. Francis of Assisi kneels before the cross in front of the Virgin Mary, whilst Petronius stands on the other side in brocaded episcopal vestments, with an altar boy holding his crosier behind him[3], blocking the viewer's view of John the Evangelist behind them[1].
Gallery
 Print of the painting by Orazio Samacchini (1566-1568), in Basilica di Santa Maria dei Servi in Bologna
Print of the painting by Orazio Samacchini (1566-1568), in Basilica di Santa Maria dei Servi in Bologna Ercole Procaccini, Madonna in glory with the patron saints of Bologna, 1570-1580, Bologna, Chiesa di San Giovanni in Monte
Ercole Procaccini, Madonna in glory with the patron saints of Bologna, 1570-1580, Bologna, Chiesa di San Giovanni in Monte Pellegrino Tibaldi, Annunciation of the Birth of John the Baptist, 1551-1553, Bologna, Basilica di San Giacomo Maggiore
Pellegrino Tibaldi, Annunciation of the Birth of John the Baptist, 1551-1553, Bologna, Basilica di San Giacomo Maggiore Bartolomeo Passarotti, Madonna in glory with saints, circa 1570, Bologna, Basilica di San Petronio
Bartolomeo Passarotti, Madonna in glory with saints, circa 1570, Bologna, Basilica di San Petronio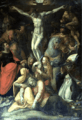 Prospero Fontana, Crucifixion, circa 1580, Museo del Convento di San Giuseppe, Bologna
Prospero Fontana, Crucifixion, circa 1580, Museo del Convento di San Giuseppe, Bologna Bartolomeo Cesi, Crucifixion with saints, 1584, Basilica di San Martino, Bologna
Bartolomeo Cesi, Crucifixion with saints, 1584, Basilica di San Martino, Bologna
References
- Daniele Benati, in Daniele Benati and Eugenio Riccomini (edited by), Annibale Carracci, Catalog of the exhibition Bologna and Rome 2006-2007 , Milan, 2006, p. 136.
- D. Benati, Annibale Carracci, Catalogo, cit., p. 136.
- Anton W. A. Boschloo, Annibale Carracci in Bologna: visible reality in art after the Council of Trent, L'Aia, 1974, pp. 1-11.