Coriocella nigra
Coriocella nigra is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Velutinidae. An Indo-Pacific species, it lives on rocks at depths of up to 15 m. It is up to 10 cm long and has an internal shell; body color is black or brown. C. nigra is probably a predator of tunicates.
| Coriocella nigra | |
|---|---|
 | |
| C. nigra heading left | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Clade: | Caenogastropoda |
| Clade: | Hypsogastropoda |
| Order: | Littorinimorpha |
| Superfamily: | Velutinoidea |
| Family: | Velutinidae |
| Genus: | Coriocella |
| Species: | C. nigra |
| Binomial name | |
| Coriocella nigra Blainville, 1824[1] | |
| Synonyms[2][3] | |
| |
Taxonomy
This species was described as Coriocella nigra by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1824 and he placed it in the newly established genus Coriocella as its only species at that time.[1] Coriocella nigra is the type species of the genus Coriocella.[5] Nowadays, at least six other species are recognized in the genus Coriocella and Blainville's binomial name is still treated as valid and in use.[6]
Distribution
The distribution of Coriocella nigra is Indo-Pacific[7] and includes South Africa,[8] Mozambique, Kenya,[9] Madagascar, Mauritius,[3] Réunion,[10] Mayotte, Gulf of Aden,[3] Gulf of Elat,[11] South Button Island,[12] Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia,[9] Papua New Guinea,[13] northern Australia and eastern Australia,[14][15] Philippines,[16] Palau,[9] Society Islands in French Polynesia,[17] New Caledonia,[18] Japan,[19] and Hawaii.[20] The type locality is Isle de France (Mauritius).[1]
Description
The color of the body may vary from uniformly velvety black to brown.[16][21] The mantle is broadly tuberculate.[16] The borders of the mantle are delicate, notched in front and spreading out widely. The foot is small and oval.[22] There are four or five lobes or bosses on the dorsal part of its body.[3][16] There is an inhalant siphon extended in the middle of the front part of the body.[20] The tentacles are triangular, granulated and are spotted with white.[20][3] There are brown eyes at the base of the tentacles. The front part of the foot is grooved. There is a jaw and a radula with 48 teeth in the mouth.[3] The body length is usually about 80 mm.[14] The body length varies from 15–18 mm up to 10 cm.[3][21] The width of the body is 8–10 mm (in body length 15–18 mm).[3]
C. nigra has an internal and reduced shell, and spirally rolled radula, as have all the members of the family Velutinidae.[13] The shell is conchinous and it has 2½ or three whorls.[14][3] Whorls are expanding rapidly and the last whorl cover four fifths of the shell height. The color of the shell is translucent white. The shell is smooth with irregular growth lines. The aperture is large.[14] Shell width is 6.3 mm (for a shell length of 10 mm). Shell length varies from 10 mm to 30–40 mm.[3][23]
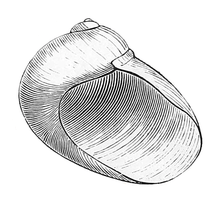 Drawing of an apertural view of a shell of C. nigra. |
 Photo of a shell. Shell length is 19 mm. |
 Photo of a shell. Shell length is 8–9 mm. |
Ecology
It lives on rocky habitats. On Hawaii it lives among Halimeda kanaloana.[20] In Australia it inhabits intertidal and subtidal zone .[14] It has been reported from depths of 1–4 m,[20] to 12 m and to 15 m.[12][19]
C. nigra is carnivorous. Its probable prey are tunicates,[13] including tunicates from the family Didemnidae in Hawaii. Its fecal pellets are oval and layered.[20] Sclerites of Octocorallia have also been found in its gut.[3]
The ostracod Pontocypria coriocellae lives as an occasional commensal in the oral tube of C. nigra.[13]
The shell of C. nigra is sometimes used by a hermit crab, Clibanarius virescens.[8]
Staurosporines 4′-N-demethyl-11-hydroxystaurosporine and 3,11-dihydroxystaurosporine have been isolated from C. nigra.[24]
References
- Blainville H. M. D. de. (1824). "Mollusques, Mollusca". In: Dictionnaire des Sciences Naturelles (F. Cuvier, ed.), vol. 32. Levrault, Strasbourg et Paris, & Le Normant, Paris. 1–392. page 259. (1825). page 466, plate 42, figure 1.
- Bouchet, P. (2011). Coriocella nigra Blainville, 1824. In: MolluscaBase (2017). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=567311 on 2017-10-02
- Marcus Ev. & Marcus Er. (1970). "Some gastropods from Madagascar and West Mexico". Malacologia 10(1): 181-223.
- Bergh L. S. R. (1853). "Bidrag til en monographi af Marseniaderne, en Familie af de Gastraeopode Mollusker. En critisk, zootomisk, zoologisk Undersmgelse". Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes-Selskabs Skrifter, Naturvidenskabelig og Mathematisk Afdeling. 5(3): 239–359, 5 pls. page 343, table 5, figure 2.
- Taki I. (1972). "ON A NEW SPECIES OF LAMELLARIA (L. UTINOMII, N. SP.) FROM SHIRAHAMA, WAKAYAMA PREFECTURE, JAPAN (MOLL., GASTROPODA)". PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIOLOGICAL LABORATORY 21(1): 1–12. PDF.
- Marshall, B.; Bouchet, P. (2016). Coriocella Blainville, 1824. In: MolluscaBase (2017). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=456342 on 2017-10-05
- Ciavatta M. L., Lefranc F., Carbone M., Mollo E., Gavagnin M., Betancourt T., Dasari R., Kornienko A. & Kiss R. (2017). "Marine Mollusk‐Derived Agents with Antiproliferative Activity as Promising Anticancer Agents to Overcome Chemotherapy Resistance". Medicinal research reviews 37(4): 702–801. doi:10.1002/med.21423.
- Nakin M. D. V. & Somers M. J. (2007). "Shell availability and use by the hermit crab Clibanarius virescens along the eastern Cape coast, South Africa". Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae 53(2): 149–155.
- "Coriocella nigra" Archived 2017-10-06 at the Wayback Machine. NidiPixel, accessed 5 October 2017.
- (in French) "Famille des LAMELLARIIDAE Orbigny, 1841." VIE OCEANE, last change 3 March 2009, accessed 5 October 2017.
- Marcus E. D. B. R. (1986). "On Coriocella nigra (Blainville, 1824), gastropoda prosobranchia Lamellariidae, from the Gulf of Elat". Israel Journal of Zoology 34(1–2), 1–11.
- Kumar J. Y., Raghunathan C. & Venkataraman K. (2015). "Research Article A report on some symbiotic shrimps (Crustacea: Decapoda) from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India". Sch. Acad. J. Biosci. 3(1B): 113–119. PDF.
- Wouters K. (1991). "A new species of the genus Pontocypria (Crustacea, Ostracoda), commensal of a lamellariid gastropod". ''Bulletin. Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique. Mededelingen. Koninklijk Belgisch Instituut voor Natuurwetenschappen 61: 65–71. PDF.
- Beechey D. (2017). "Coriocella nigra". The Seashells of New South Wales, last change 14 April 2017, accessed 5 October 2017.
- "Coriocella nigra map". Atlas of Living Australia, accessed 5 october 2017.
- Gosliner T. M. (2006). "Marine Gastropoda collected by the Steamer Albatros from the Phlippines in 1908". Records of the Western Australian Museum 'Supplement, 69: 83–93. PDF.
- Tröndlé J. & Boutet M. (2009). "Inventory of marine molluscs of French Polynesia". Atol Research Bulletin 570: 1-87.
- Héros V., Lozouet P., Maestrati P., von Cosel R., Brabant D. & Bouchet P. (2007). "Mollusca of New Caledonia". In: Payri, C. & Richer De Forges, B. (Eds) Compendium of marine species of New Caledonia. Doc. Sci. Tech. IRD, Nouméa. II7(2): 199–254. PDF.
- Rudman W. B. (Oct 5 1999). "Comment on Coriocella nigra from Japan by H. Ono". [Message in] Sea Slug Forum. Australian Museum, Sydney. Available from http://www.seaslugforum.net/find/1400 Accessed 5 october 2017.
- Pittman C. & Fiene P. "Coriocella nigra". Sea Slugs of Hawaii by Cory Pittman & Pauline Fiene. Accessed 5 october 2017.
- (in French) Coriocelle noire". DORIS, accessed 5 october 2017.
- Penny Cyclopaedia of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge. C. Knight. 1837. p. 93.
- "Coriocella nigra". Gastropods.com. Retrieved 5 October 2017.
- Cantrell C. L., Groweiss A., Gustafson K. R. & Boyd M. R. (1999). "A new staurosporine analog from the prosobranch mollusk Coriocella nigra". Natural Product Letters 14: 39–46. doi:10.1080/10575639908045433.
External links
- Vayssière A. (1911). "Recherches zoologiques et anatomiques sur les Opisthobranches de Ia Mer Rouge et du Golfe d'Aden". Annales de la Faculté des Sciences de Marseille tom. 20(Suppl.), fasc. 2: 1–157, pis. 1–11. Plate 11, fig. 167.
- Wellens W. (1998). "Redescription of Coriocella nigra de Blainville 1825 and Chelyonotus tonganus Quoy and Gaimard 1832 (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia: Lamellariidae)". Journal of Conchology 36: 43–61.
- (in Japanese) 沼波秀樹, 関田梨恵 & 荒井碧. (2007). "P16. 殻が内在するイボベッコウタマガイ (腹足綱: ハナヅトガイ科) の生き残り戦略 (日本貝類学会平成 19 年度大会 (豊橋) 研究発表要旨)". Venus: journal of the Malacological Society of Japan 66(1): 122. CiNii.
- Tryon G. W. (1882). Structural and systematic conchology: an introduction to the study of the Mollusca. volume I, Philadelphia, published by the author. plate 62, figure 62-63.
- Beechey F. W. (1839). "The zoology of Captain Beechey's voyage". London. page 133.
- Chenu J. C. (1859–1862) "Manuel de conchyliologie et paléontologie conchlyliologique". t. 1–2. Paris. page 212
- Coriocella nigra video
- Photos of Coriocella nigra on Sealife Collection