Continuous stirred-tank reactor
The continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR), also known as vat- or backmix reactor, mixed flow reactor (MFR), or a continuous-flow stirred-tank reactor (CFSTR), is a common model for a chemical reactor in chemical engineering and environmental engineering. A CSTR often refers to a model used to estimate the key unit operation variables when using a continuous agitated-tank reactor to reach a specified output. The mathematical model works for all fluids: liquids, gases, and slurries.

The behavior of a CSTR is often approximated or modeled by that of an ideal CSTR, which assumes perfect mixing. In a perfectly mixed reactor, reagent is instantaneously and uniformly mixed throughout the reactor upon entry. Consequently, the output composition is identical to composition of the material inside the reactor, which is a function of residence time and reaction rate. The CSTR is the ideal limit of complete mixing in reactor design, which is the complete opposite of a plug flow reactor (PFR). In practice, no reactors behave ideally but instead fall somewhere in between the mixing limits of an ideal CSTR and PFR.
Ideal CSTR
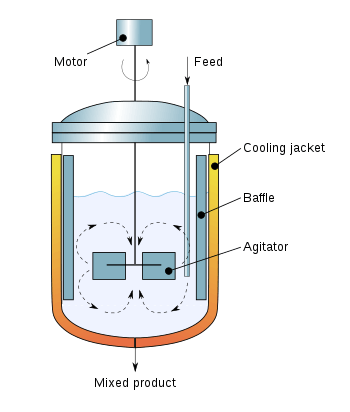
Modeling
A continuous fluid flow containing non-conservative chemical reactant A enters an ideal CSTR of volume V.
Assumptions:
- perfect or ideal mixing
- steady state , where NA is the number of moles of species A
- closed boundaries
- constant fluid density (valid for most liquids; valid for gases only if there is no net change in the number of moles or drastic temperature change)
- nth-order reaction (r = kCAn), where k is the reaction rate constant, CA is the concentration of species A, and n is the order of the reaction
- isothermal conditions, or constant temperature (k is constant)
- single, irreversible reaction (νA = −1)
- All reactant A is converted to products via chemical reaction
- NA = CA V
Integral mass balance on number of moles NA of species A in a reactor of volume V:
where,
- FAo is the molar flow rate inlet of species A
- FA is the molar flow rate outlet of species A
- vA is the stoichiometric coefficient
- rA is the reaction rate
Applying the assumptions of steady state and νA = −1, Equation 2 simplifies to:
The molar flow rates of species A can then be rewritten in terms of the concentration of A and the fluid flow rate (Q):
Equation 4 can then be rearranged to isolate rA and simplified:
where,
- is the theoretical residence time ()
- CAo is the inlet concentration of species A
- CA is the reactor/outlet concentration of species A
Residence time is the total amount of time a discrete quantity of reagent spends inside the reactor. For an ideal reactor, the theoretical residence time, , is always equal to the reactor volume divided by the fluid flow rate.[2] See the next section for a more in-depth discussion on the residence time distribution of a CSTR.
Depending on the order of the reaction, the reaction rate, rA, is generally dependent on the concentration of species A in the reactor and the rate constant. A key assumption when modeling a CSTR is that any reactant in the fluid is perfectly (i.e. uniformly) mixed in the reactor, implying that the concentration within the reactor is the same in the outlet stream.[3] The rate constant can be determined using a known empirical reaction rate that is adjusted for temperature using the Arrhenius temperature dependence.[2] Generally, as the temperature increases so does the rate at which the reaction occurs.
Equation 6 can be solved by integration after substituting the proper rate expression. The table below summarizes the outlet concentration of species A for an ideal CSTR. The values of the outlet concentration and residence time are major design criteria in the design of CSTRs for industrial applications.
| Reaction Order | CA |
|---|---|
| n=0 | |
| n=1 | [1] |
| n=2 | |
| Other n | Numerical solution required |
Residence time distribution

An ideal CSTR will exhibit well-defined flow behavior that can be characterized by the reactor's residence time distribution, or exit age distribution.[4] Not all fluid particles will spend the same amount of time within the reactor. The exit age distribution (E(t)) defines the probability that a given fluid particle will spend time t in the reactor. Similarly, the cumulative age distribution (F(t)) gives the probability that a given fluid particle has an exit age less than time t.[3] One of the key takeaways from the exit age distribution is that a very small number of fluid particles will never exit the CSTR.[5] Depending on the application of the reactor, this may either be an asset or a drawback.
Non-ideal CSTR
While the ideal CSTR model is useful for predicting the fate of constituents during a chemical or biological process, CSTRs rarely exhibit ideal behavior in reality.[2] More commonly, the reactor hydraulics do not behave ideally or the system conditions do not obey the initial assumptions. Perfect mixing is a theoretical concept that is not achievable in practice.[6] For engineering purposes, however, if the residence time is 5-10 times the mixing time, the perfect mixing assumption generally holds true.

Non-ideal hydraulic behavior is commonly classified by either dead space or short-circuiting. These phenomena occur when some fluid spends less time in the reactor than the theoretical residence time, . The presence of corners or baffles in a reactor often results in some dead space where the fluid is poorly mixed.[6] Similarly, a jet of fluid in the reactor can cause short-circuiting, in which a portion of the flow exits the reactor much quicker than the bulk fluid. If dead space or short-circuiting occur in a CSTR, the relevant chemical or biological reactions may not finish before the fluid exits the reactor.[2] Any deviation from ideal flow will result in a residence time distribution different from the ideal distribution, as seen at right.
Modeling non-ideal flow
Although ideal flow reactors are seldom found in practice, they are useful tools for modeling non-ideal flow reactors. Any flow regime can be achieved by modeling a reactor as a combination of ideal CSTRs and plug flow reactors (PFRs) either in series or in parallel.[6] For examples, an infinite series of ideal CSTRs is hydraulically equivalent to an ideal PFR.[2]
To model systems that do not obey the assumptions of constant temperature and a single reaction, additional dependent variables must be considered. If the system is considered to be in unsteady-state, a differential equation or a system of coupled differential equations must be solved. Deviations of the CSTR behavior can be considered by the dispersion model. CSTRs are known to be one of the systems which exhibit complex behavior such as steady-state multiplicity, limit cycles, and chaos.
Applications
CSTRs facilitate rapid dilution of reagents through mixing. Therefore, for non-zero-order reactions, the low concentration of reagent in the reactor means a CSTR will be less efficient at removing the reagent compared to a PFR with the same residence time.[3] Therefore, CSTRs are typically larger than PFRs, which may be a challenge in applications where space is limited. However, one of the added benefits of dilution in CSTRs is the ability to neutralize shocks to the system. As opposed to PFRs, the performance of CSTRs is less susceptible to changes in the influent composition, which makes it ideal for a variety of industrial applications:

Environmental engineering
- Activated sludge process for wastewater treatment[2]
- Lagoon treatment systems for natural wastewater treatment[2]
- Anaerobic digesters for the stabilization of wastewater biosolids[7]
Chemical engineering
- Loop reactor for pharmaceutical production[8]
- Fermentation[8]
- Biogas production
Notes
References
- Schmidt, Lanny D. (1998). The Engineering of Chemical Reactions. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-510588-5.
- Metcalf & Eddy (2013-09-03). Wastewater engineering : treatment and resource recovery. Tchobanoglous, George,, Stensel, H. David,, Tsuchihashi, Ryujiro,, Burton, Franklin L. (Franklin Louis), 1927-, Abu-Orf, Mohammad,, Bowden, Gregory (Fifth ed.). New York, NY. ISBN 978-0-07-340118-8. OCLC 858915999.
- Benjamin, Mark M. (2013-06-13). Water quality engineering : physical/chemical treatment processes. Lawler, Desmond F. Hoboken, New Jersey. ISBN 978-1-118-63227-7. OCLC 856567226.
- Bolin, Bert; Rodhe, Henning (January 1973). "A note on the concepts of age distribution and transit time in natural reservoirs". Tellus. 25 (1): 58–62. doi:10.3402/tellusa.v25i1.9644. ISSN 0040-2826.
- Monsen, Nancy E.; Cloern, James E.; Lucas, Lisa V.; Monismith, Stephen G. (September 2002). "A comment on the use of flushing time, residence time, and age as transport time scales". Limnology and Oceanography. 47 (5): 1545–1553. Bibcode:2002LimOc..47.1545M. doi:10.4319/lo.2002.47.5.1545.
- Davis, Mark E. (2003). Fundamentals of chemical reaction engineering. Davis, Robert J. (International ed.). Boston: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-1-62870-437-2. OCLC 880604539.
- Hurtado, F.J.; Kaiser, A.S.; Zamora, B. (March 2015). "Fluid dynamic analysis of a continuous stirred tank reactor for technical optimization of wastewater digestion". Water Research. 71: 282–293. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2014.11.053. ISSN 0043-1354. PMID 25635665.
- "Visual Encyclopedia of Chemical Engineering". encyclopedia.che.engin.umich.edu. Retrieved 2020-04-30.