Component (graph theory)
In graph theory, a component, sometimes called a connected component, of an undirected graph is a subgraph in which any two vertices are connected to each other by paths, and which is connected to no additional vertices in the supergraph. For example, the graph shown in the illustration has three components. A vertex with no incident edges is itself a component. A graph that is itself connected has exactly one component, consisting of the whole graph.
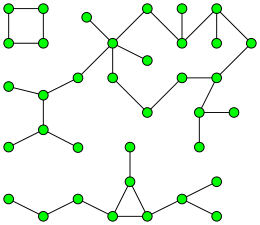
An equivalence relation
An alternative way to define components involves the equivalence classes of an equivalence relation that is defined on the vertices of the graph. In an undirected graph, a vertex v is reachable from a vertex u if there is a path from u to v. In this definition, a single vertex is counted as a path of length zero, and the same vertex may occur more than once within a path. Reachability is an equivalence relation, since:
- It is reflexive: There is a trivial path of length zero from any vertex to itself.
- It is symmetric: If there is a path from u to v, the same edges form a path from v to u.
- It is transitive: If there is a path from u to v and a path from v to w, the two paths may be concatenated together to form a path from u to w.
The components are then the induced subgraphs formed by the equivalence classes of this relation.
The number of components
The number of components is an important topological invariant of a graph. In topological graph theory it can be interpreted as the zeroth Betti number of the graph. In algebraic graph theory it equals the multiplicity of 0 as an eigenvalue of the Laplacian matrix of the graph. It is also the index of the first nonzero coefficient of the chromatic polynomial of a graph. Numbers of components play a key role in the Tutte theorem characterizing graphs that have perfect matchings, and in the definition of graph toughness.
Algorithms
It is straightforward to compute the components of a graph in linear time (in terms of the numbers of the vertices and edges of the graph) using either breadth-first search or depth-first search. In either case, a search that begins at some particular vertex v will find the entire component containing v (and no more) before returning. To find all the components of a graph, loop through its vertices, starting a new breadth first or depth first search whenever the loop reaches a vertex that has not already been included in a previously found component. Hopcroft & Tarjan (1973) describe essentially this algorithm, and state that at that point it was "well known".
There are also efficient algorithms to dynamically track the components of a graph as vertices and edges are added, as a straightforward application of disjoint-set data structures. These algorithms require amortized O(α(n)) time per operation, where adding vertices and edges and determining the component in which a vertex falls are both operations, and α(n) is a very slow-growing inverse of the very quickly growing Ackermann function. A related problem is tracking components as all edges are deleted from a graph, one by one; an algorithm exists to solve this with constant time per query, and O(|V||E|) time to maintain the data structure; this is an amortized cost of O(|V|) per edge deletion. For forests, the cost can be reduced to O(q + |V| log |V|), or O(log |V|) amortized cost per edge deletion (Shiloach & Even 1981).
Researchers have also studied algorithms for finding components in more limited models of computation, such as programs in which the working memory is limited to a logarithmic number of bits (defined by the complexity class L). Lewis & Papadimitriou (1982) asked whether it is possible to test in logspace whether two vertices belong to the same component of an undirected graph, and defined a complexity class SL of problems logspace-equivalent to connectivity. Finally Reingold (2008) succeeded in finding an algorithm for solving this connectivity problem in logarithmic space, showing that L = SL.
Components in random graphs
In random graphs the sizes of components are given by a random variable, which, in turn, depends on the specific model.
The model has three regions with seemingly different behavior:
Subcritical : All components are simple and very small, the largest component has size ;
Critical : ;
Supercritical : where is the positive solution to the equation
where and are respectively the largest and the second largest components. All other components have their sizes of the order
See also
- Giant component
- Strongly connected component, a related concept for directed graphs
- Biconnected component
- Modular decomposition, for a proper generalization of components on undirected graphs
- Connected-component labeling, a basic technique in computer image analysis based on components of graphs
- Percolation theory, a theory describing the behavior of components in random subgraphs of grid graphs
- Centrality
- Bridge (graph theory)
References
- Hopcroft, J.; Tarjan, R. (1973), "Algorithm 447: efficient algorithms for graph manipulation", Communications of the ACM, 16 (6): 372–378, doi:10.1145/362248.362272
- Lewis, Harry R.; Papadimitriou, Christos H. (1982), "Symmetric space-bounded computation", Theoretical Computer Science, 19 (2): 161–187, doi:10.1016/0304-3975(82)90058-5
- Reingold, Omer (2008), "Undirected connectivity in log-space", Journal of the ACM, 55 (4): Article 17, 24 pages, doi:10.1145/1391289.1391291
- Shiloach, Yossi; Even, Shimon (1981), "An on-line edge-deletion problem", Journal of the ACM, 28 (1): 1–4, doi:10.1145/322234.322235
External links
- MATLAB code to find components in undirected graphs, MATLAB File Exchange.
- Connected components, Steven Skiena, The Stony Brook Algorithm Repository