ColorChecker
The ColorChecker Color Rendition Chart (often referred to by its original name, the Macbeth ColorChecker[1] or simply Macbeth chart[2]) is a color calibration target consisting of a cardboard-framed arrangement of 24 squares of painted samples. The ColorChecker was introduced in a 1976 paper by McCamy, Marcus, and Davidson in the Journal of Applied Photographic Engineering.[3] The chart’s color patches have spectral reflectances intended to mimic those of natural objects such as human skin, foliage, and flowers, to have consistent color appearance under a variety of lighting conditions, especially as detected by typical color photographic film, and to be stable over time.


Design
The ColorChecker Classic chart is a rectangular card measuring about 11 by 8.25 inches (27.9 by 21.0 cm), or in its original incarnation about 13 by 9 inches (33 by 23 cm), an aspect ratio approximately the same as that of 35 mm film.[4] It includes 24 patches in a 4 × 6 grid, each slightly under 2 inches (5.1 cm) square, made of matte paint applied to smooth paper, and surrounded by a black border. Six of the patches form a uniform gray lightness scale, and another six are primary colors typical of chemical photographic processes – red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, and yellow. The remaining colors include approximations of medium light and medium dark human skin, blue sky, the front of a typical leaf, and a blue chicory flower. The rest were chosen arbitrarily to represent a gamut "of general interest and utility for test purposes", though the orange and yellow patches are similarly colored to typical oranges and lemons.[3]
There is also a ColorCheckerPassport, a smaller version of the ColorChecker Classic with the same 24 chips but in a tri-fold version with some additional patches on two of the pages. Its dimensions are 125 mm (H) × 90 mm (W) × 9 mm (T). The pigments for ColorCheckerPassport were modified in November 2014, so the current available cards do not have exactly the same carnation, and hence RGB numbers, as before, and particularly are not the ones provided on next section.
Colors
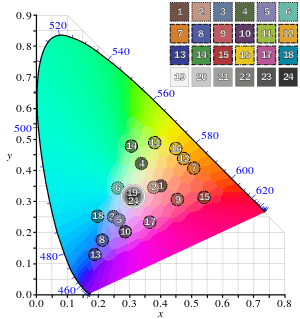
The colors of the chart were described by McCamy et al. with colorimetric measurements using the CIE 1931 2° standard observer and Illuminant C, and also in terms of the Munsell color system. Using measured reflectance spectra, it is possible to derive CIELAB coordinates for Illuminants D65 and D50 and coordinates in sRGB.[5]
| Index | Description | Munsell Notation | CIE xyY | Manufacturer's sRGB D50 color values[7] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row 1: Natural colors | ||||
| 1 | Dark skin | 3 YR 3.7/3.2 | 0.400 0.350 10.1 | #735244 |
| 2 | Light skin | 2.2 YR 6.47/4.1 | 0.377 0.345 35.8 | #c29682 |
| 3 | Blue sky | 4.3 PB 4.95/5.5 | 0.247 0.251 19.3 | #627a9d |
| 4 | Foliage | 6.7 GY 4.2/4.1 | 0.337 0.422 13.3 | #576c43 |
| 5 | Blue flower | 9.7 PB 5.47/6.7 | 0.265 0.240 24.3 | #8580b1 |
| 6 | Bluish green | 2.5 BG 7/6 | 0.261 0.343 43.1 | #67bdaa |
| Row 2: Miscellaneous colors | ||||
| 7 | Orange | 5 YR 6/11 | 0.506 0.407 30.1 | #d67e2c |
| 8 | Purplish blue | 7.5 PB 4/10.7 | 0.211 0.175 12.0 | #505ba6 |
| 9 | Moderate red | 2.5 R 5/10 | 0.453 0.306 19.8 | #c15a63 |
| 10 | Purple | 5 P 3/7 | 0.285 0.202 6.6 | #5e3c6c |
| 11 | Yellow green | 5 GY 7.1/9.1 | 0.380 0.489 44.3 | #9dbc40 |
| 12 | Orange yellow | 10 YR 7/10.5 | 0.473 0.438 43.1 | #e0a32e |
| Row 3: Primary and secondary colors | ||||
| 13 | Blue | 7.5 PB 2.9/12.7 | 0.187 0.129 6.1 | #383d96 |
| 14 | Green | 0.25 G 5.4/9.6 | 0.305 0.478 23.4 | #469449 |
| 15 | Red | 5 R 4/12 | 0.539 0.313 12.0 | #af363c |
| 16 | Yellow | 5 Y 8/11.1 | 0.448 0.470 59.1 | #e7c71f |
| 17 | Magenta | 2.5 RP 5/12 | 0.364 0.233 19.8 | #bb5695 |
| 18 | Cyan | 5 B 5/8 | 0.196 0.252 19.8 | #0885a1 |
| Row 4: Grayscale colors | ||||
| 19 | White | N 9.5/ | 0.310 0.316 90.0 | #f3f3f2 |
| 20 | Neutral 8 | N 8/ | 0.310 0.316 59.1 | #c8c8c8 |
| 21 | Neutral 6.5 | N 6.5/ | 0.310 0.316 36.2 | #a0a0a0 |
| 22 | Neutral 5 | N 5/ | 0.310 0.316 19.8 | #7a7a79 |
| 23 | Neutral 3.5 | N 3.5/ | 0.310 0.316 9.0 | #555555 |
| 24 | Black | N 2/ | 0.310 0.316 3.1 | #343434 |

Use
Color targets such as the ColorChecker can be captured by cameras and other color input devices, and the resulting images’ output can be compared to the original chart, or to reference measurements, to test the degree to which image acquisition reproduction systems and processes approximate the human visual system’s. It can also be used to color correct one photo with the chart in it (that may have a different color cast, for example due to a lighting coloration difference) to another "reference" photo with the chart in it. Because of its wide availability and use, its careful design, and its consistency, and because comprehensive spectrophotometric measurements are available, the ColorChecker has also been used in academic research into topics such as spectral imaging.[8]
ColorChecker Digital SG
X-Rite also sells a 140-patch chart called the ColorChecker Digital SG, and is intended for automated use with computer software to characterize digital cameras and scanners.
See also
- List of colors
- Color chart
- Color calibration
- Color management
- Color mapping
- ICC profile
- IT8
References
- The ColorChecker was originally produced by Macbeth (then a subsidiary of Kollmorgen), which through a series of mergers and acquisitions now belongs to X-Rite.
- "Computational Color Imaging – Alain Trémeau – Google Books". Retrieved 12 October 2015.
- C. S. McCamy, H. Marcus, and J. G. Davidson (1976). "A Color-Rendition Chart". Journal of Applied Photographic Engineering 2(3). 95–99.
- Charles Poynton (2008). "ColorChecker (‘Macbeth’) Chart". poynton.com
- Measured reflectance spectra are available Archived 10 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine from the Munsell Color Science Laboratory website in html Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine and Excel Archived 21 November 2014 at the Wayback Machine formats, taken from measurements published in Noboru Ohta (1997). "The Basis of Color Reproduction Engineering" (Japanese). Corona-sha Company of Japan.
See also Danny Pascale’s page. - Field, Gary G. (1990), Color Scanning and Imaging Systems, Pittsburgh, PA: Graphic Arts Technical Foundation, ISBN 0-88362-120-7
- ColorChecker Colorimetric Data (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on 18 April 2012, retrieved 17 April 2012
- For example, Roy S. Berns and Lawrence A. Taplin (2006). "Practical Spectral Imaging Using a Color-Filter Array Digital Camera".
External links
- "ColorChecker Classic" official product page at the X-Rite website for the full size, 24 patch version of the chart.
- ColorChecker Passport official product page for the small, 24 patch version of the chart.
- "ColorChecker Digital SG" official product page for the full size, 140 patch version of the chart
- Danny Pascale (2009). "The ColorChecker (since 1976!)". Babelcolor.com. This extensive page includes a history of the chart, average spectrophotometric measurements from 20 ColorCheckers (the precise tools used for these measurements is unclear), calculated RGB values in a variety of RGB color spaces, a list of places to buy charts, and advice for using the data in practical camera calibration and image applications.
- Danny Pascale (2006) "RGB coordinates of the Macbeth ColorChecker". Includes comparisons in CIELAB and RGB values based on spectrophotometric measurements vs. provided by Gretag–Macbeth
- Bruce Lindbloom (2007). "How the ColorChecker Calculator Works". brucelindbloom.com. Lindbloom measured the spectral reflectances his own copy of the ColorChecker, and created a Java applet to calculate colorimetric coordinates under various standard illuminants and in various RGB color spaces
- Bruce Lindbloom (2008). "ColorChecker RGB Summaries, Spreadsheets and Lab TIFF File". brucelindbloom.com. A page showing RGB values for color patches in various RGB color spaces, based on the applet described above, and a set of Excel spreadsheets for comparing these numbers to those in a digital camera or scanner image of the ColorChecker.