Qullasuyu
Qullasuyu (Aymara: Qullasuyu ![]()

Overview
Recently, there have been movements to form a "Greater Qullasuyu" (or Qullana Suyu Marka) which would incorporate a territory similar to the former Tawantinsuyu in extent. This ideal has been proposed by the office of the Apu Mallku and the parliament of the Qullana. Qullasuyu was the largest of the four suyu (or "quarters", the largest divisions of the Inca empire) in terms of area. This suyu encompassed the Bolivian Altiplano and much of the southern Andes, running down into Argentina and as far south as the Maule river near modern Santiago, Chile.[2] Along with Kuntisuyu, it was part of the Hurin Suyukuna or "Lower Quarters" of the empire.[3][4]
Wamani
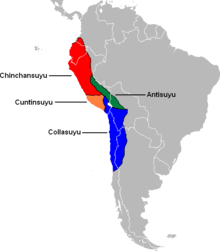
Each suyu was divided into wamani, or provinces. Qullasuyu included the wamani of:
- Arica or Arika
- Cana or Kana
- Canche or Kanche
- Caranga or Karanka
- Caruma
- Cavina or Kawina, whose people were “Incas by privilege”
- Chicha
- Cochabamba or Quchapampa
- Collagua
- Lipe
- Locumba
- Lupaqa
- Moquegua
- Pacajes or Pacasa
- Qolla Urcosuyu or Qulla Urqusuyu
- Sama
- Tambo or Tampu
- Tarata
- Ubina
- Yampará or Yampara
See also
- Organization of the Inca Empire
- Chinchaysuyu
- Antisuyu
- Kuntisuyu
- Oroncota, Yampara settlement and Inca fortress in Bolivia
- The Chilean Inca Trail
References
- Teofilo Laime Ajacopa, Diccionario Bilingüe Iskay simipi yuyayk'ancha, La Paz, 2007 (Quechua-Spanish dictionary)
- D’Altroy, Terence N. (2005). The Incas. Blackwell Publishing: Malden, p. 86-87
- D’Altroy, Terence N. (2005). The Incas. Blackwell Publishing: Malden, p. 42-43, 86-89
- Steward, Julian H. & Faron, Louis, C. (1959). Native Peoples of South America. McGraw-Hill: New York, p. 185-192
- D’Altroy, Terence N. (2005). The Incas. Blackwell Publishing: Malden, p. 42-43, 86-89
- Steward, Julian H. & Faron, Louis, C. (1959). Native Peoples of South America. McGraw-Hill: New York, p. 185-192
Template:Peoples of the Americas-stub