Closed-loop transfer function
A closed-loop transfer function in control theory is a mathematical expression (algorithm) describing the net result of the effects of a closed (feedback) loop on the input signal to the circuits enclosed by the loop.
Overview
The closed-loop transfer function is measured at the output. The output signal waveform can be calculated from the closed-loop transfer function and the input signal waveform.
An example of a closed-loop transfer function is shown below:
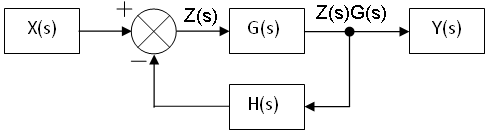
The summing node and the G(s) and H(s) blocks can all be combined into one block, which would have the following transfer function:
is called feedforward transfer function, is called feedback transfer function, and their product is called the Open loop transfer function.
Derivation
We define an intermediate signal Z (also known as error signal) shown as follows:

Using this figure we write:
Now, plug the second equation into the first to eliminate Z(s):
Move all the terms with Y(s) to the left hand side, and keep the term with X(s) on the right hand side:
Therefore,
See also
- Federal Standard 1037C
- Open-loop controller
- Open-Loop Transfer Function
References
