Clemente Susini
Clemente Michelangelo Susini (1754–1814) was an Italian sculptor who became renowned for his wax anatomical models, vividly and accurately depicting partly dissected corpses. These models were praised by both doctors and artists.
Clemente Michelangelo Susini | |
|---|---|
Medallion of Clemente Susini | |
| Born | 1754 Florence |
| Died | 1814 (aged 59–60) Florence |
| Nationality | Florentine |
| Occupation | Sculptor |
| Known for | Wax anatomical models |
Biography
Clemente Michelangelo Susini was born in 1754. He studied sculpture at the Royal Gallery in Florence.[1] In 1771 Felice Fontana asked Leopold, Grand Duke of Tuscany to provide financial support for a workshop to prepare wax models for use in teaching anatomy. The workshop was part of the Natural History Museum, and later was called La Specola. The first modeler was Giuseppe Ferrini.[2] Susini joined the wax-modelling workshop in 1773.[3] He was given medical direction by Fontana.[4] Susini had become the chief modeler at the workshop by 1782. His work included models of animals as well as of human anatomy.[1]
In 1780 Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, brother of the Grand Duke of Tuscany, visited the museum. He was profoundly impressed by the models, perceiving the value they would provide to students of medicine, and ordered a set of models.[3] The work was undertaken between 1781 and 1786, and consisted of about 1000 wax sculptures. The models were based in part on anatomical drawings, in part on corpses dissected by anatomists such as Felice Fontana and Paolo Mascagni. These were carried by a train of hundreds of mules to Vienna, where they were exhibited at the "Josephinum", the Museum of the Medical University of Vienna. They still may be seen there.[5]
As the result of the Austrian commission, Susini's work became much in demand from surgeons and anatomists. Susini organized his workshop to produce large volumes of models, which were shipped throughout Italy and beyond. The use of iron supports rather than natural skeletons let the workshop produce models more quickly and economically than other workshops. In 1799 Susina was appointed a professor at the Accademia di Belle Arti of Florence, where he taught the drawing of nudes, while continuing to run his workshop. He was employed by the anatomist Paolo Mascagni to model Mascagni's many discoveries of the anatomy of the lymphatic system.[3]
Susini died in 1814.[3] He had made or overseen the production of more than 2,000 models.[2] Of these, the Josephinum in Vienna holds 1,192 wax models in six rooms.[6] Another major collection, formerly held by the University of Cagliari, is now held by the Museo archeologico nazionale in the Piazza Arsenale of Cagliari, Sardinia, where they are on display in a pentagonal room.[7]
Work
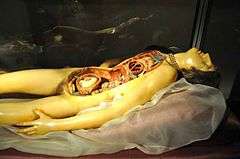
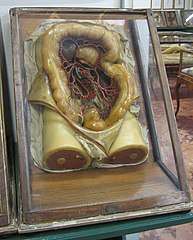
Susini's models present anatomy, as understood at the time, in a highly realistic form. Some of his figures are also quite artistic sculptures.[3] His obituary praised him for "the beauty which he gave to the most revolting things."[1] In 1780 his models drew praise for their accuracy from Adolph Murray, professor of anatomy at Uppsala University, while the neo-classical sculptor Antonio Canova praised them for their artistic merit.[3] Georges Didi-Huberman considered that Susini's Vénus anatomique was more an artistic masterpiece than a medical one.[8]
The Venerina ("little Venus"), at the Anatomy and Obstetrics Museum in the Palazzo Poggi, Bologna, is a sensual model of the body of a young pregnant woman whose trunk holds removable layers that reveal her internal organs.[9] Another group of models held in Bologna show the hearing and lymphatic systems.[3] Some of Susini's most important works are in Cagliari, created from dissections by the anatomist Francesco Antonio Boi of the University of Cagliari. They highlight the nerves and, unlike Susini's less accurate earlier models, do not show lymphatic vessels in the brain. It is clear that Susini and Boi worked closely together to ensure a high level of anatomical accuracy. The Cagliari models, with their expressive faces, are also artistic masterpieces.[2]
Gallery
A collection of Susini's models from the Specola museum is shown below.
Bibliography
- Susini, Clemente (1813). Gabinetto d'anatomia umana e comparata eseguita in cera. Carli. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
References
Citations
Sources
- Camedda, Gigi (2012). "Clemente Susini (1754-1814)". Science Museum. Archived from the original on 2012-08-07. Retrieved 2013-01-10.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Clemente Michelangelo Susini" (in Italian). Università di Bologna. Archived from the original on 2013-02-18. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
- "Clemente Susini's "Venerina" anatomical wax model". Museo di Palazzo Poggi. Retrieved 2013-01-12.
- Kemp, Martin; Wallae, Marina (2000). Spectacular Bodies: The Art and Science of the Human Body from Leonardo to Now. University of California Press. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-520-22792-7. Retrieved 2013-01-10.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Marquer, Bertrand (2008). Les romans de la Salpêtrière: réception d'une scénographie clinique. Librairie Droz. ISBN 978-2-600-01153-2. Retrieved 2013-01-10.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Museum of the Medical University". Welcome to Vienna!. WienTourismus. Retrieved 2013-01-13.
- Pollier-Green, Pascale; Van De Velde, A.; Pollier, Chantal (2009-05-30). Confronting Mortality with Art and Science: Scientific and Artistic Impressions on What the Certainty of Death Says About Life. Asp / Vubpress / Upa. ISBN 978-90-5487-443-0. Retrieved 2013-01-10.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Riva, A. (2012-01-04). "University of Cagliari: The evolution of anatomical illustration and wax modelling in Italy from the 16th to early 19th centuries". Issues in Anatomy, Physiology, Metabolism, Morphology, and Human Biology: 2011 Edition. ScholarlyEditions. ISBN 978-1-4649-6477-0. Retrieved 2013-01-10.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Riva, Alessandro; Baghino, Attilio (June–August 2001). "Historia de las ceras anatómicas de Cagliari en Cerdeña". Elementos. 8 (42). Archived from the original on 2014-12-21. Retrieved 2013-01-12.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
Further reading
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Clemente Susini. |
- Cattaneo, Luigi; Riva, Alessandro (1993). Anatomical waxes by Clemente Susini of the University of Cagliari. Edizioni della Torre. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
- Susini, Clemente; Riva, Alessandro; Cattaneo, Luigi (2007). Flesh & wax: the Clemente Susini's anatomical models in the University of Cagliari. Ilisso. ISBN 978-88-89188-97-2. Retrieved 2013-01-10.