Chino Creek
Chino Creek is a major stream of the Pomona Valley, in the western Inland Empire region of Southern California. It is a tributary of the Santa Ana River.
| Chino Creek | |
|---|---|
 View downstream from Central Avenue bridge in Chino Hills | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Counties | Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside |
| District | Pomona Valley |
| Cities | Pomona, Chino, Chino Hills |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Southern Pomona |
| • location | Los Angeles County |
| • coordinates | 34°02′12″N 117°45′29″W[1] |
| • elevation | 780 ft (240 m) |
| Mouth | Santa Ana River |
• location | Riverside County |
• coordinates | 33°54′08″N 117°38′35″W[1] |
• elevation | 489 ft (149 m) |
| Length | 12.7 mi (20.4 km), Southeast |
| Basin size | 218 sq mi (560 km2) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Schaefer Avenue, near Chino[2] |
| • average | 19.9 cu ft/s (0.56 m3/s)[2] |
| • minimum | 0 cu ft/s (0 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 12,700 cu ft/s (360 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Santa Ana River basin |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | San Antonio Creek, Mill Creek (Chino Creek) |
| • right | Little Chino Creek |
Geography
Although the main stem is short at about 12.7 miles (20.4 km), it drains an extensive basin of 218 square miles (560 km2) from the San Gabriel Mountains to the Santa Ana River near Corona. The creek's watershed spans three counties, with the majority in San Bernardino County, and parts of seven incorporated cities.
The drainage basin is intensely developed for residential, industrial, and agricultural use. As a result, the creek and its tributaries are heavily polluted, and receive effluents from multiple wastewater treatment plants and drains. Agricultural pollution from the raising of livestock in the creek's lower basin is the largest source of contamination. There are efforts to control nuisance flows and pollutants in the lower part of the creek to protect the wetlands in the Prado Flood Control Basin, an important ecological area.
Course
Chino Creek rises from underground in a storm water channel flowing southwards from a subdivision in southern Pomona, eastern Los Angeles County.
The concrete channelized stream soon enters southwestern San Bernardino County and runs generally southeast across the Chino Valley between the Chino Hills to the south, and the city of Chino to the northeast. One of the creek's main tributaries, San Antonio Creek, comes in from the left about 2 miles (3.2 km) downstream of Pomona. San Antonio Creek originates in the San Gabriel Mountains, and drains the northern part of the Chino basin, and its course is longer above their confluence than Chino Creek.[3]
From there the creek flows roughly parallel to the Chino Valley Freeway (State Route 71) southeast, through a predominantly industrial and agricultural area of Chino. About 6 miles (9.7 km) above the mouth, the streambed changes from a concrete culvert to an earthen channel. The river then enters the El Prado Golf Course and turns south. The last portion of the creek is predominantly marshland, situated within the Prado Flood Control Basin behind the Prado Dam, and mostly in Riverside County. The main affluent, Mill Creek, joins from the left within the Prado Basin. Chino Creek then runs south to its confluence with the Santa Ana River just north of the dam about 2.5 miles (4.0 km) east-northeast of Corona.[3]
Geology
The creek runs along the southwest side of the gently sloping alluvial Cucamonga Plain comprising sediments deposited by erosion from the San Gabriel Mountains. It essentially follows the southern outline of the combined alluvial fans of San Antonio, Mill/Cucamonga, Deer, and other tributary streams flowing from the range across the Pomona Valley. Before urbanization Chino Creek was a perennial stream, although most of its tributaries were ephemeral. The impermeable bedrock of the Chino Hills, which abut the southwest edge of the watershed, forced groundwater percolating southwards from the San Gabriels to rise to the surface, thus ensuring a stable year round flow even in years of drought.[4]
Historically, the waters of upper San Antonio Creek, Mill Creek, and other streams flowing from the San Gabriels disappeared into the ground about 10 to 15 miles (16 to 24 km) north of Chino Creek, only to reappear within a few miles of the main stream, providing most of its flow.[5] The deposits by the San Gabriel streams are generally hundreds of feet deep and gradually decrease in coarseness in a southerly direction. These tributaries originally joined Chino only during extreme floods.[4] Before channelization, San Antonio Creek was recognized as the upper section of Chino Creek, as the first water in the latter stream rose to the surface at their confluence.[6]
Watershed
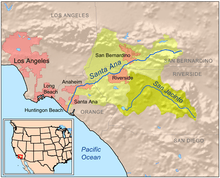
The drainage basin of Chino Creek spans 218 square miles (560 km2) in parts of Los Angeles, San Bernardino and Riverside Counties, with the vast majority within southwestern San Bernardino County. The broad, flat watershed comprises much of the southeastern slopes of the San Gabriel Mountains and alluvial plains that lie to the south of the range.[7] Almost 55 percent of the basin is heavy urban development, and major cities include Rancho Cucamonga, Ontario, Upland, Pomona and Chino. ~20% of the watershed is wild land, mostly in the mountainous north within the Angeles National Forest, and the remaining quarter in the south is used for agriculture, much for the raising of livestock.
The largest tributaries of Chino Creek are San Antonio Creek and Mill Creek (called Cucamonga Creek in San Bernardino County), both of which are longer than the main stem. Other tributaries include Little Chino Creek and an unnamed left fork that drains a large area south of Chino and north of the El Prado Golf Course. To the west the Chino Creek drainage basin borders on the San Gabriel River watershed, specifically the tributaries of that river, Coyote Creek, Walnut Creek, San Jose Creek and the East Fork San Gabriel River. To the east lies the basin of Etiwanda Creek, a tributary of the Santa Ana; to the northeast is Lytle Creek, another Santa Ana tributary stream.
The Chino Creek watershed is notable for containing the heaviest concentration of dairy farms in the United States. A 50-square-mile (130 km2) area of farmland in the southern part of the basin was found to have up to 400,000 cows in a study by the Regional Water Quality Control Board. Waste generated on these farms has led to severely raised nitrate and salinity levels in the creek.[8] The Chino Creek Wetlands conservation area was established at the creek's mouth in 2008 in an effort to filter pollutants in the stream. The preserve comprises 22 acres (8.9 ha) and includes artificial wetlands irrigated with water from the creek.[9]
History and human usage
From the 1770s through the 1830s the creek's watershed in Pomona Valley was part of the grazing lands of the Mission San Gabriel Arcángel herds. In 1841 much of the creek course became part of Rancho Santa Ana del Chino, a Mexican land grant in Alta California.
In the late 1800s, the first American settlers arrived in the area and established small towns along the creek's confluence with the Santa Ana River, including Rincon (later changed to Prado).[10] Agricultural development in the large, flat bowl of land adjoining the land between Chino Creek and the Santa Ana River, known as the Chino Basin, was heavy because of the region's rich soils, smooth topography and abundant water resources. Citrus, alfalfa and sugar beets made up most of the agricultural production.[11] Dams were constructed on Chino Creek and miles of irrigation laterals laid, but due to the stream's low flows and tendency for flash floods the system as a whole was not extremely efficient.
By the 20th century steady urban development of the basin led to increased flooding risk because of urban runoff problems, and floods were causing more damage to property adjoining streams. In the 1960s upper Chino Creek and most of its tributaries were channelized with concrete to allow faster passage of floodwaters, but this essentially caused the ecological devastation of the creek. Currently the channelized sections of lower Chino Creek have a design capacity of roughly 53,000 cubic feet per second (1,500 m3/s). The San Antonio Dam was constructed in 1956 by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to control floods from upper San Antonio Creek.[12]
Crossings
Crossings of the creek are listed going downstream. Tributary entry points are also included to clarify locations.
|
|
|
See also
References
- "Chino Creek". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. 1981-01-19. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- "USGS Gage #11073360 on Chino Creek at Schaefer Avenue near Chino, CA" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2009. Retrieved 2015-01-28.
- USGS Topo Maps for United States (Map). Cartography by United States Geological Survey. ACME Mapper. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- Pardee, George Cooper; et al. (1912). Report of the Conservation Commission of the state of California: January 1, 1913. F.W. Richardson. pp. 269–270.
- U.S. Geological Survey (1912). Water-supply paper. G.P.O. p. 49.
- United States, Office of Experiment Station (1910). Bulletin, Volumes 231-236. G.P.O.
- "Middle Santa Ana River Watershed". Middle Santa Ana River TMDL Task Force. Santa Ana Watershed Project Authority. Archived from the original on 2011-07-28. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- "Santa Ana River Watershed Subprofiles". Southern California Wetlands Recovery Project Information Station. Archived from the original on 2010-11-11. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
- "Water Discovery Field Trip Program at the Chino Creek Wetlands and Educational Park" (PDF). Santa Ana Watershed Association. Inland Empire Utilities Agency. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-26. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
- Mitchell, Patrick (2006). Santa Ana River Guide: From Crest to Coast - 110 Miles Along Southern California's Largest River System. Wilderness Press. ISBN 0-89997-411-2.
- Pardee et al., pp. 270-271
- "Pomona Valley Protective Association Overview". Pomona Valley Protective Association. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
