Chauffeur's fracture
Chauffeur's fracture, also known as Hutchinson fracture, is a type of fracture of the forearm, specifically the radial styloid process. The injury is typically caused by compression of the scaphoid bone of the hand against the styloid process of the distal radius. It can be caused by falling onto an outstretched hand. Treatment is often open reduction and internal fixation, which is surgical realignment of the bone fragments and fixation with pins, screws, or plates.
| Chauffeur's fracture | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hutchinson fracture, backfire fracture |
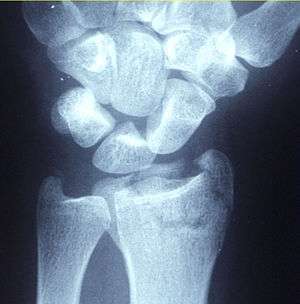 | |
| X-ray of a displaced intra-articular distal radius fracture in an external fixator. The articular surface is widely displaced and irregular. This is a Chauffeur's fracture. Frykman class 3. | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic |
The name originates from early chauffeurs who sustained these injuries when the car back-fired while the chauffeur was hand-cranking to start the car. The back-fire forced the crank backward into the chauffeur's palm and produced the characteristic styloid fracture.[1][2]
References
- Greenspan, A: Orthopaedic Imaging: A Practical Approach, page 170. Edition 4, 2004, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-5006-7
- "Fractures of the Radius in Starting Automobiles", Lund, F. B., M.D., Boston Med Surg J 1904; 151:481-483, Printed November 3, 1904
External links
| Classification |
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.