Caucasotachea vindobonensis
Caucasotachea vindobonensis is a species of medium-sized air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod in the family Helicidae.
| Caucasotachea vindobonensis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| (unranked): | clade Heterobranchia clade Euthyneura clade Panpulmonata clade Eupulmonata clade Stylommatophora informal group Sigmurethra |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Caucasotachea |
| Species: | C. vindobonensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Caucasotachea vindobonensis (C. Pfeiffer, 1828)[2] | |
The scientific name is derived from the Celtic settlement Vindobona, now known as Vienna, the capital of Austria. This species was assigned to the genus Cepaea for a long time. However, molecular biologist research[3][4] showed, that it is not closely related to Cepaea, but belongs in fact to the genus Caucasotachea.[5]
Description
The right-coiled, globular shell of C. vindobonensis is about 17–21 mm high and 20–25 mm broad with 5,5-6 whorls.[6] The umbilicus is completely covered in adult specimens. The lip is always red-brown at the inner and outer side with a fine white stripe at its margin. This specific lip coloration allows to separate it from the conchological similar Cepaea hortensis (pure white lip) and Cepaea nemoralis (consistent dark brown lip), with which C. vindobonensis often co-occurs. The shell is whitish or yellowish, with about 5 brown stripes, the upper two are usually weak. The lowermost stripe is quite near to the covered umbilicus. There is a slight variation of shell coulour within this species (see below). The animal itself is yellowish with grey tentacles.
Examples of shell variation within C. vindobonensis:
Distribution and habitat
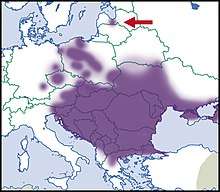
The distribution of this species is Pontic, Pannonian and Balkanian.[7][8]
It occurs in Albania,[1] Austria,[1] Bulgaria, Bosnia and Herzegovina,[1] Croatia,[1] Czech Republic[1] (near threatened (NT)[9] Its westernmost, but non-indigenous, record is from Western Bohemia.[10]), Germany (reintroduced[1]), Greece[1]), Hungary,[1] Italy,[1] Latvia,[11] Macedonia,[1] Moldova,[1] Poland,[1] Romania,[1] Slovakia,[1] Slovenia,[1] Russia (Rostov Oblast, Stavropol Krai, Krasnodar Krai, Moscow Region - non-indigenous distribution[12]) and Ukraine[13][1]
The original habitat of C. vindobonensis was most probably open forests on the Balkans, from where it spread over large parts of Central and Eastern Europe after the last glaciation.[8] Nevertheless, it also dwells in several grassland habitats like meadows, steppe and ruderal areas, especially in the north of its distribution area. The highest vertical occurrence is about 1600 m asl in Southern Bulgaria.[6]
Life cycle
All the following information originates from a Greek study. [14] Because Greece is in the southernmost part of the distribution area, the phenology for this species might be quite difference in the more northerly countries where it is found. According to the Greek study, C. vindobonensis becomes mature after its second year, and can reach a maximum life span of about 7 years. The reproductive period in Greece lasts from April to June, with a maximum in May. About 29-67 eggs are laid, having a diameter about 3 mm, and the juveniles hatch out after 18 days. During hot summer days, these snails rest attached to leaves or the stems of tall plants. Hibernation commences at the end of October to the beginning of November, and the snails come out of hibernation in March.
References
- Neubert E. (2011). "Cepaea vindobonensis". In: IUCN 2013. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Downloaded on 26 May 2014.
- Pfeiffer C (1828). Naturgeschichte deutscher Land- und Süsswasser-Mollusken. Third. Weimar: Landes-Industrie-Comptoir. pp. I–VI [= 1–6], 1–84, Taf. I–VIII [= 1–8].
- Neiber MT, Hausdorf B (December 2015). "Molecular phylogeny reveals the polyphyly of the snail genus Cepaea (Gastropoda: Helicidae)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 93: 143–9. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2015.07.022. PMID 26256642.
- Neiber MT, Sagorny C, Hausdorf B (February 2016). "Increasing the number of molecular markers resolves the phylogenetic relationship of 'Cepaea'vindobonensis (Pfeiffer 1828) with Caucasotachea Boettger 1909 (Gastropoda: Pulmonata: Helicidae)". Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research. 54 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1111/jzs.12116.
- "Taxon details: Caucasotachea vindobonensis (c. Pfeiffer, 1828)". WoRMS. Retrieved 16 January 2019.
- Welter-Schultes FW (2012). Bestimmungsbuch für europäische Land- und Süsswassermollusken A1-A3 S., 679 S., Q1-Q78 S. [European non-marine molluscs, a guide for species identification] (in German). Göttingen: Planet Poster Editions. p. 268. ISBN 978-3-933922-75-5.
- Lisický MJ (1991). Mollusca Slovenska [The Slovak molluscs] (in Slovak). Bratislava: VEDA vydavateľstvo Slovenskej akadémie vied. pp. 344.
- Kajtoch Ł, Davison A, Grindon A, Deli T, Sramkó G, Gwardjan M, et al. (September 2017). "Caucasotachea vindobonensis (Gastropoda: Helicidae)". Organisms, Diversity & Evolution. 17 (3): 679–692. doi:10.1007/s13127-017-0337-3. PMC 5965669. PMID 29805298.
- "Red List of the molluscs (Mollusca) of the Czech Republic". Malacologica Bohemoslovaca.
- Dvořák L, Hlaváč JČ (2013). "Páskovka Cepaea vindobonensis (Pulmonata: Helicidae) v západních Čechách" [The snail Cepaea vindobonensis (Pulmonata: Helicidae) in West Bohemia] (PDF). Malacologica Bohemoslovaca (in Slovak). 12: 99–104.
- Stalažs A, Šteffek J, Dreijers E (2008). "Cepaea vindobonensis (C. Pfeiffer, 1828) in Latvia" (PDF). Acta Universitatis Latviensis. 745: 199–203.
- Egorov R. (2014). "The first record of Cepaea vindobonensis (Pfeiffer, 1828) (Stylommatophora: Helicidae) in the central part of European Russia". Malacologica Bohemoslovaca 13: 110-113. PDF.
- Balashov I, Gural-Sverlova N (August 2012). "An annotated checklist of the terrestrial molluscs of Ukraine". Journal of Conchology. 41: 91–109.
- Staikou AE (1998). "Aspects of life cycle, population dynamics, growth and secondary production of the pulmonate snail Cepaea vindobonensis (Férussac, 1821) in northern Greece". Journal of Molluscan Studies. 64 (3): 297–308. doi:10.1093/mollus/64.3.297.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cepaea vindobonensis. |

