Cascabel (artillery)
A cascabel is a subassembly of a muzzle-loading cannon, a knob to which to attach arresting ropes to deal with the recoil of firing the cannon.
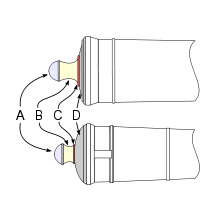

Description
A cannon's cascabel comprises the knob (A) and the neck (B), with some models also having a filet (C). By some definitions the cascabel additionally includes the base of the breech (D). Cascabels varied in design and appearance, and were a common feature of cannons from the 17th century until the advent of the breech loading cannon in the late 19th century. Many naval guns had a heavy metal loop on the cascabel, the pomellion, through which a wide rope was passed.[1]
Bronze cascabels from captured guns have been used to make Victoria Cross medals. It was long thought that Russian guns captured during the Siege of Sevastopol were used, but this has been shown not to be so.[2]
References
- "The Development of Artillery". Gibraltar National Museum. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- Tom White (3 May 2020). "Show your mettle: Victoria Cross not made of captured Russian guns after all". TheObserver.
Ripley, Warren (1984), Artillery and Ammunition of the Civil War, Charleston, S.C.: The Battery Press, p. 353
Manucy, Albert (1985), Artillery Through the Ages: A Short Illustrated History of Cannon, Emphasizing Types Used in America, Washington, D.C.: National Park Service, retrieved 2007-11-06.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cascabel (artillery). |