Caruncle (bird anatomy)
A caruncle is defined as 'a small, fleshy excrescence that is a normal part of an animal's anatomy'.[1] Within this definition, caruncles in birds include wattles (or dewlaps), combs, snoods, and earlobes. The term caruncle is derived from Latin caruncula, the diminutive of carō, "flesh".[2]
Taxonomy
Caruncles are carnosities, often of bright colors such as red, blue, yellow or white. They can be present on the head, neck, throat, cheeks or around the eyes of some birds. They may be present as combs or crests and other structures near the beak, or, hanging from the throat or neck. Caruncles may be featherless, or, have small scattered feathers. In some species, they may form pendulous structures of erectile tissue, such as the "snood" of the domestic turkey.[3][4][5]
Caruncles are sometimes secondary sexual characteristics, having a more intense color or even a different color, developing as the male reaches sexual maturity.
Function
Caruncles are also ornamental elements used by males to attract females to breeding.[6] Having large caruncles or colorful bright ones indicates high levels of testosterone, that they are well-fed birds able to elude other predators thus showing the good quality of their genes.[7] It has been proposed that these organs are also associated with genes which encode resistance to disease.[7] It is believed that for birds living in tropical regions, the caruncles also play a role in thermoregulation, making the blood cool faster when flowing through them.[8]
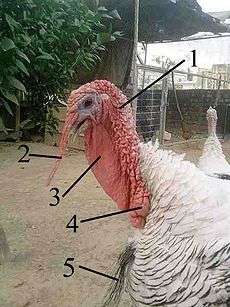
Turkeys

In turkeys, the term usually refers to small, bulbous, fleshy protuberances found on the head, neck and throat, with larger structures particularly at the bottom of the throat. The wattle is a flap of skin hanging under the chin connecting the throat and head and the snood is a highly erectile appendage emanating from the forehead. Both sexes of turkey possess caruncles, although they are more pronounced in the male. Usually they are pale, but when the male becomes excited or during courtship, the caruncles, wattle and snood all engorge with blood, become bright red or blue, and enlarge.[9]
The beard (a tuft of modified brush-like feathers) also becomes erect.
Muscovy ducks
In the context of Muscovy ducks, caruncles refer to the red fleshy mask that surrounds the head of adult birds, particularly prominent in adult drakes (males).[10]
Birds with caruncles
Many species from a variety of families have caruncles, including:
- Phasianidae (pheasants, roosters and turkeys)
- Cathartidae (condors and vultures)
- Falconidae (falcons)
- Accipitridae (eagles and vultures)
- Casuariidae (cassowaries)
- Ciconiidae (storks)
- Threskiornithidae (ibises and spoonbills)
- Charadriidae (lapwings)
- Anatidae (swans, ducks and geese)
- Cuculidae (cuckoos and relatives)
- Musophagidae (turacos)
- Cacatuidae (cockatoos)
- Psittacidae (parrots and macaws)
- Coliidae (mousebird)
- Callaeidae (kokako, saddleback and huia)
- Campephagidae (lobotos)
- Meliphagidae (honeyeaters)
- Picathartes (white-necked rockfowl)
- Platysteiridae (black-throated wattle-eye)
- Tyrannidae (indian silverbill)
Gallery
 Roosters often have large crests.
Roosters often have large crests. The mountain caracara, like many hawks, has carunculated features.
The mountain caracara, like many hawks, has carunculated features. The saddlebacks from New Zealand have wattles hanging from the sides of their beak.
The saddlebacks from New Zealand have wattles hanging from the sides of their beak. The king vulture has multi-colored wattles.
The king vulture has multi-colored wattles.- The head and neck of the cassowary are covered with blue and two red wattles hanging from them.
- The face of the Muscovy duck is covered with red wattles.
References
- Lexic.us. "Definition of caruncle". Retrieved April 20, 2013.
- Merriam-Webster. "Caruncle". Retrieved April 20, 2013.
- Sharpe, Richard Bowdler (1888). Catalogue of the birds in the British Museum. British Natural History Museum Department of Zoology.
- "Caruncle definition". Word Reference Dictionary. Retrieved 2014-05-16.
- Audubon, John James; Amadon, Dean; Bull, John L. (1967). The Birds Of America. Dover Publications. OCLC 555150.
- Burke, Don (2005). The Complete Burke's Backyard: The Ultimate Book of Fact Sheets. p. 702. ISBN 9781740457392.
- Baratti, Mariella; Ammannati, Martina; Magnelli, Claudia; Massolo, Alessandro; Dessì-Fulgheri, Francesco (2010). "Are large wattles related to particular MHC genotypes in the male pheasant?". Genetica. 138 (6): 657–665. doi:10.1007/s10709-010-9440-5. PMID 20145977.
- Buchholz, Richard (1996). Thermoregulatory Role of the Unfeathered Head and Neck in Male Wild Turkeys (PDF). Sora.unm.edu. p. 311.
- Graves, R.A. (2005). "Know your turkey parts". Retrieved April 20, 2013.
- Heritage Poultry Breeders Association of America (2013). "Muscovy Ducks". Retrieved April 20, 2013.
External links
