Carnosol
Carnosol is a phenolic diterpene found in the herbs rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis)[1] and Mountain desert sage (Salvia pachyphylla).[2]
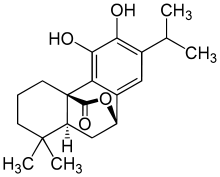 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H26O4 | |
| Molar mass | 330.424 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It has been studied in-vitro for anti-cancer effects in various cancer cell types.[3]
References
- Ai-Hsiang Lo; Yu-Chih Liang; Shoei-Yn Lin-Shiau; Chi-Tang Ho; Jen-Kun Lin (2002). "Carnosol, an antioxidant in rosemary, suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase through down-regulating nuclear factor-κB in mouse macrophages". Carcinogenesis. 23 (6): 983–991. doi:10.1093/carcin/23.6.983. PMID 12082020.
- Ivan C. Guerrero; Lucia S. Andres; Leticia G. Leon; Ruben P. Machin; Jose M. Padron; Javier G. Luis; Jose Delgadillo (2006). "Abietane Diterpenoids from Salvia pachyphylla and S. clevelandii with Cytotoxic Activity against Human Cancer Cell Lines". J. Nat. Prod. 69 (12): 1803–1805. doi:10.1021/np060279i. PMID 17190465.
- Johnson JJ (June 2011). "Carnosol: a promising anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory agent". Cancer Lett. 305 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.02.005. PMC 3070765. PMID 21382660.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.