Carboxycyclophosphamide
Carboxycyclophosphamide is an inactive metabolite of the cytotoxic antineoplastic drug cyclophosphamide. In the metabolic pathway of cyclophosphamide inactivation it first metabolizes to 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide, then partially tautomerizes into aldophosphamide. Aldophosphamide then, in turn, is oxidized into carboxycyclophosphamide by the enzyme ALDH (aldehyde dehydrogenase).[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
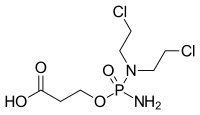
| IUPAC name
3-({amino[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phosphoryl}oxy)propanoic acid | |
| Other names
Carboxyphosphamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H15Cl2N2O4P | |
| Molar mass | 293.084762 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Dockham, PA; Lee, MO; Sladek, NE (1992). "Identification of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenases that catalyze the oxidation of aldophosphamide and retinaldehyde". Biochem Pharmacol. 43: 2453–69. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(92)90326-e. PMID 1610409.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.