Camille Flammarion Observatory
The observatory was established in Juvisy-sur-Orge in 1883 by the French astronomer and author Camille Flammarion. In March 2010, the structure was classified as a historical monument by the French Ministry of Culture. The observatory belongs to the Société astronomique de France.
 | |||
| Alternative names | Juvisy Observatory | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Named after | Camille Flammarion | ||
| Organization | Société astronomique de France | ||
| Observatory code | 285 | ||
| Location | 32, avenue de la Cour-de-France, Juvisy-sur-Orge, near Paris, France | ||
| Coordinates | 48.6898°N 2.3986°E | ||
| Altitude | 100 m | ||
| Established | 1883 | ||
| Telescopes | |||
| |||
 Location of Camille Flammarion Observatory | |||
Building and grounds
The observatory is located on Route nationale 7 (formerly the avenue de la Cour de France), close to the downtown of Juvisy. The site, which is on a prominent hilltop location, is a large parcel of land that contains several buildings, a monumental gate, gardens, and a small forest.

The building housing the observatory was originally a post house constructed in 1730. In 1883–1884, Flammarion transformed the structure into an astronomical observatory by adding a large equatorial room for the telescope, a library, a scientific museum, a meteorological station and an agricultural research station.[1]
In 1899, the architect François Giamarchi was commissioned to transform the east façade of the building (garden side) by adding a decorative relief of ionic columns supporting a cornice.[2]
In 1910, Flammarion installed a vertical sundial on the upper level of the observatory. The sundial was restored in 1998 and 1972.[3]
In March 2010, the French Ministry of Culture classified the building and the large gate as protected historical monuments.[4]
Flammarion's second wife, Gabrielle Renaudot Flammarion, bequeathed the entire site to the Société Astronomique de France upon her death in 1962. In 1971, the society signed a 99-year lease with the municipality of Juvisy to ensure the site's maintenance, preservation and accessibility. Today, the society organises regular observations at the observatory for the general public.[5]
Telescope

The 5 meter dome was constructed by the engineer Adolphe Gilon. It houses Camille Flammarion's equatorial mount refracting telescope, which has a diameter of 240 mm and a focal length of 3600 mm. The telescope was built by Denis Albert Bardou, a Parisian optics manufacturer. Flammarion's choice of the telescope was inspired by a similar instrument in the west tower of the Paris Observatory.[6]
Scientific contribution
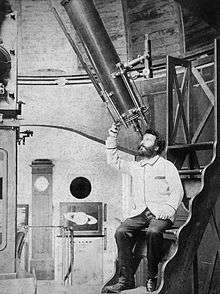
Astronomers who conducted research at the observatory included:
- Camille Flammarion, astronomer, from 1883–1925.
- Eugène Michael Antoniadi, assistant astronomer,[7] 1891[8]
- Anton Schmoll, June 1892[8]
- E. Mabire, from 6 June - 12 July 1892[8]
- Ferdinand Quénisset, observer,[9] from 1–31 May 1892, and August 1892[8]
- Léon Guiot, from 20 August - 14 September 1892[8]
- Ferdinand Quénisset, from 1 May - 1 September 1893[8]
- Lucien Rudaux, June 1893[8]
- Léon Guiot, from 2 August - 4 October 1893[8]
- Gaston Millochau, from 1–30 September 1893[8]
- Eugène Michael Antoniadi, from 27 August - 1 November 1894[8]
- Eugène Michael Antoniadi, from 31 May - 28 September 1896[8]
- Eugène Michael Antoniadi, from 31 January - 19 August 1897[8]
- Antonin Benoit, assistant astronomer,[10] from 9 September - 6 December 1902, from 23 May - 21 July 1904, from 3 August 1904 - 13 April 1905[8]
- Ferdinand Quénisset, from 15 October – 23 December 1906[8]
- Ferdinand Quénisset, assistant astronomer, from 1906–1947.[11]
- Gabrielle Renaudot Flammarion, astronomer, from 1925–1962.
The results of their research at the observatory were published in numerous articles and photographs in L'Astronomie, the journal of the Société astronomique de France.
605 Juvisia
In 1906, German astronomer Max Wolf discovered a minor planet orbiting the Sun and named it 605 Juvisia in honor of the location of Flammarion's observatory.
References
- Mérimée database, Monuments Historiques,French Ministry of Culture
- "Observatoire Camille-Flammarion" (IA91000720), Région Ile-de-France - Inventaire général du patrimoine culturel.
- Mélanie Desmeules. "Camille Flammarion (1842-1925), le cadranier d'un seul cadran."Le Gnomoniste (La Commission des Cadrans solaires du Québec), Vol. 9, No. 1, Mars 2002, page 6.
- "Liste des immeubles protégés au titre des monuments historiques en 2009," Journal officiel de la République française, n°0084, 10 April 2010, page 6840.
- Mairie de Juvisy-sur-Orge, "L’observatoire Camille Flammarion," http://juvisy.fr/votre-ville/patrimoine, consulted 15 March 2018.
- Colette Aymard et Laurence-Anne Mayeur, « L’observatoire de Juvisy-sur-Orge, l’« univers d’un chercheur » à sauvegarder », In Situ [online], 29 | 2016, published 13 July 2016, consulted 16 June 2017.
- Touchet, E. “La Vie et L'Oeuvre de Camille Flammarion. L'Astronomie 1925, vol. 39, p. 354.
- Carnets d'observations. “Archives et manuscrits de l'Observatoire de Paris : Fonds Eugène Michel Antoniadi : Ms 1138”, Alidade
- L'Astronomie 1951, vol. 65, p. 356.
- “BENOIT, Antonin.” P. Véron, Dictionnaire des astronomes français 1850-1950., www.obs-hp.fr/dictionnaire/
- P. Véron, dictionnaire des astronomes français 1850-1950, www.obs-hp.fr/dictionnaire/
See also
- List of observatories