Cimlanod
Cimlanod (development codes CXL-1427 and BMS-986231) is an experimental drug for the treatment of acute decompensated heart failure. It was discovered by Cardioxyl Pharmaceuticals, which was acquired by Bristol-Myers Squibb. It is a nitroxyl donor.[1]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
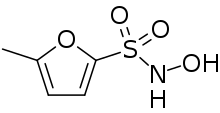
| Formula | C5H7NO4S |
| Molar mass | 177.17 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Cimlanod is a prodrug of CXL-1020.[2]
A preliminary study showed efficacy in patients with class III and IV heart failure.[3] A phase II clinical trial was completed in 2016.[4]
References
- Alternative Names: BMS-986231; CXL 1427; HNO Donor. "BMS 986231 - AdisInsight". Adisinsight.springer.com. Retrieved 2017-05-22.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Alternative Names: CXL-1020. "CXL 1020 - AdisInsight". Adisinsight.springer.com. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- http://www.mdedge.com/ecardiologynews/article/109035/heart-failure/nitroxl-prodrug-shows-promise-acute-heart-failure
- "A Dose Ranging Phase IIa Study of 6 Hour Intravenous Dosages of CXL-1427 in Patients Hospitalized With Heart Failure - Full Text View". ClinicalTrials.gov. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.