Butyryl chloride
Butyryl chloride is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2C(O)Cl. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Butyryl chloride is soluble in aprotic organic solvents, but it reacts readily with water and alcohols. It is usually produced by chlorination of butyric acid.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butanoyl chloride | |
| Other names
Butyryl chloride n-Butyryl chloride C-4 Acyl halide butanoyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.999 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2353 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7ClO | |
| Molar mass | 106.55 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Odor | pungent |
| Density | 1.033 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −89 °C (−128 °F; 184 K) |
| Boiling point | 102 °C (216 °F; 375 K) |
| decomposition | |
| Solubility | miscible with ether |
| -62.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.412 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Reacts violently with water, flammable, corrosive |
| GHS pictograms |  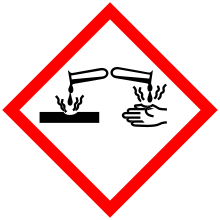 |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H314 |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P370+378, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 21.7 °C (71.1 °F; 294.8 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Reactions
Like related acyl chlorides, butyryl chloride hydrolyzes readily:
- CH3CH2CH2C(O)Cl + H2O → CH3CH2CH2CO2H + HCl
Alcohols react to give esters:
- CH3CH2CH2C(O)Cl + ROH → CH3CH2CH2CO2R + HCl
Amines react to give amides:
- CH3CH2CH2C(O)Cl + R2NH → CH3CH2CH2C(O)NR2 + HCl
Derivatives of butyryl chloride are used in manufacturing pesticides, pharmaceuticals, perfume fixative, polymerization catalyst, and dyestuffs. Butyryl chloride is also commonly used as an intermediate for organic synthesis for the preparation of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes, esters, and peroxide compounds.[2]
Safety
Butyryl chloride is flammable and fumes in air, releasing hydrogen chloride.
References
- Helferich, B.; Schaefer, W. (1929). "n-Butyryl Chloride". Org. Synth. 9: 32. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.009.0032.
- http://chemicalland21.com/specialtychem/perchem/N-BUTYRYL%20CHLORIDE.htm
