Business Process Framework (eTOM)
The Business Process Framework is an operating model framework for telecom service providers in the telecommunications industry.[1] The model describes the required business processes of service providers, and defines key elements and how they should interact.
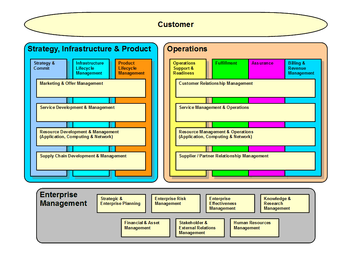
The Business Process Framework (eTOM) is a standard maintained by the TM Forum,[1] an association for service providers and their suppliers in the telecommunications and entertainment industries.
History
The development of the business process standardization for telecom service providers started with the founding of the TM Forum in 1988. The initial goal was to facilitate the creation of 'interoperable network management products'.[2] The first approved standard was the 'OSI/NM Forum Protocol Specification,' an extension of OSI protocols developed since the late 1970s.
The direct development towards the Business Process Framework (eTOM), as Brenner (2007) explained, was "the Telecom Operation Map (TOM) was first published in 2001. The goal of TOM was the creation of an industry-owned framework of business processes, including the definition of a common enterprise-independent terminology for service management. It was also supposed to serve as a basis for discussing the scope of information management necessary for the execution of the processes. The result of this latter effort has meanwhile spawned its own TMF document family, the Shared Information and Data Model (SID).[1]
The Telecom Operation Map (TOM) was extended in 2001 to eTOM, an acronym for Enhanced Telecom Operations Map.[1] The process model eTOm was renamed "Enhanced Telecom Operations Map (eTOM)," and in 2013 to "Business Process Framework (eTOM)."
There have been many versions of eTOM. Version 14 was published in May 2014. It also has been developed into a component of NGOSS, which has been renamed Frameworx.
Building blocks
Hierarchy
The Business Process Framework model consists of processes at 5 levels:
- Strategy,
- Network Operations,
- Level-2,
- Level-3,
- Level-4.
These levels form a hierarchy, with each level encapsulating a group of processes at the next level of detail.
Rows and columns
The graphic representation of a Business Process Framework (eTOM) model consists of rows and columns, the intersections of which denote specific business processes.
- The top row includes customer facing activities such as marketing,
- While the bottom row includes supplier facing and support activities.
In this manner the Business Process Framework map covers the whole value chain. The map also indicates the interaction between processes.
Three broad sections
Business Process Framework (eTOM) processes fall into three major process areas,[3] as shown in the diagram:
- Strategy, Infrastructure & Product (SIP),
- Operations and
- Enterprise Management.
- Strategy, Infrastructure & Product
-
- Columns
- Strategy and Commit, Infrastructure Lifecycle Management and Product Lifecycle Management
- Rows
- Marketing & Offer Management, Service Development & Management, Resource Development & Management and Supply Chain Development & Management
- Operations
- Columns
- Operations Support & Readiness, Fulfillment, Assurance and Billing
- Rows
- Customer Relationship Management, Service Management & Operations, Resource Management & Operations and Supplier/Partner Relationship Management.
Other standards
- The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is an analogous standard or framework for best practices in information technology.
- Both of these frameworks are part of Total Quality Management, in which industries have, since 1950, formalized their business processes and metrics in search of higher quality, fewer defects, and greater efficiency.
- ISO 9000 is another of these "process and results improvement" standards, but it is far more generic than either Business Process Framework or ITIL.
- Business Process Framework has been adopted by the ITU-T as a Recommendation and published in the M.3050.x series.
- OpenReference is a business process framework developed for product and service businesses and includes processes, metrics and practices.
References
- Brenner, Michael, et al. "Service Provisioning-Challenges, Process Alignment and Tool Support." Bergstra, J. und M. Burgess (Herausgeber): Handbook of Network and System Administration. Elsevier (2007).
- Robert Oebele Reitsma (2011) Innovating Mass-customized Service. p. 128
- "Introduction to eTOM White Paper" (PDF). www.cisco.com. 16 February 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Business Process Framework (eTOM). |
- "Business Process Framework (eTOM) R17.0.0". TM Forum. Retrieved December 11, 2017.
- ITU M.3050
- OpenReference Frameworks