British Concession (Shanghai)
The British Concession or Settlement was a foreign enclave (a "concession") in Shanghai within the Qing Empire which existed from around 1845 until its unification with the city's north-eastern American area to form the Shanghai International Settlement in 1863.
| British Concession in Shanghai | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foreign Enclave | |||||||||
| 1845–1863 | |||||||||
 Flag | |||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1845 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1863 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
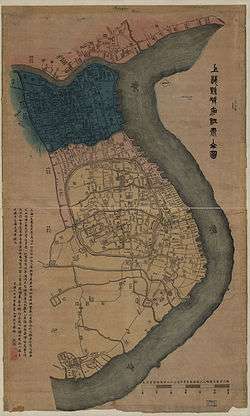
The settlement was bordered at north by the right bank of the Suzhou River before it flows into the Huangpu, at east by the Huangpu, and at south by a channel, the Yang-King-Pang which will be the future boundary with the French concession.
History
The British occupied Shanghai during the First Opium War and it was opened to foreign trade by the terms of the Treaty of Nanking. The British settlement was established by the 1845 Land Regulations, undertaken on the initiative of the intendant Gong Mujiu.[1] On 20 November 1846, a formal concession was established; this was expanded on 27 November 1848. After a proposal to make Shanghai an independent "free city" was rejected in 1862, the British area agreed to merge with the American on 21 September 1863 as the Shanghai International Settlement. This occurred in December of the same year.
See also
- Shanghai International Settlement
- American Concession (Shanghai)
- Shanghai French Concession
- List of former foreign enclaves in China
References
- Cassel, Pär (2003), "Excavating Extraterritoriality: The "Judicial Sub-Prefect" as a Prototype for the Mixed Court in Shanghai", Late Imperial China, Vol. 24, No. 2, pp. 156–182.