Breechloader
A breechloader[1][2] is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition (cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front (muzzle) end.

Modern firearms are generally breech-loading – except for replicas of vintage weapons. Early firearms up until the mid-19th century, however, were almost entirely muzzle-loading. Mortars are the only muzzleloaders remaining in frequent modern usage.
Breech-loading provides the advantage of reduced reloading time, because it is a lot quicker to load the projectile and propellant into the chamber of a gun/cannon than to reach all the way over to the front end to load ammunition and then push them back down a long tube – especially when the projectile fits tightly and the tube has spiral ridges from rifling. In field artillery, the advantages were similar – crews no longer had to get in front of the gun and force things down a long barrel with a ramrod, and the shot could now tightly fit the bore, increasing accuracy. It also made it easier to load a previously fired weapon with a fouled barrel. Gun turrets and emplacements for breechloaders can be smaller, since crews don't need to retract the gun for frontal loading.
After breech-loading became common, it also became common practice to fit recoil systems onto field guns to prevent the recoil from rolling the carriage back with every shot and ruining the aim. That provided faster firing times, but is not directly related to whether the gun is breech loading or not. Now that guns were able to fire without recoiling, the crew was able to remain grouped closely around the gun, ready to load and put final touches on the aim, subsequent to firing the next shot. That led to the development of an armored shield fitted to the carriage of the gun, to help shield the crew from long range area or sniper fire from the new, high-velocity, long-range rifles, or even machine guns.
History


Although breech-loading firearms were developed as far back as the late 14th century in Burgundy,[3] breech-loading became more successful with improvements in precision engineering and machining in the 19th century (see Dreyse needle gun).
The main challenge for developers of breech-loading firearms was sealing the breech. This was eventually solved for smaller firearms by the development of the self-contained metallic cartridge. For firearms too large to use cartridges, the problem was solved by the development of the interrupted screw.
Swivel guns
Breech-loading swivel guns were invented in the 14th century. They were a particular type of swivel gun, and consisted in a small breech-loading cannon equipped with a swivel for easy rotation, loaded by inserting a mug-shaped chamber already filled with powder and projectiles. The breech-loading swivel gun had a high rate of fire, and was especially effective in anti-personnel roles.
Firearms


Breech-loading firearms are known from the 16th century. Henry VIII possessed one, which he apparently used as a hunting gun to shoot birds.[4] Meanwhile, in China, an early form of breech loading musket, known as the Che Dian Chong, was known to have been created in the second half of the 16th century for the Ming dynasty's arsenals.[5] Like all early breech loading fireams, gas leakage was a limitation and danger present in the weapon's mechanism. [6]
More breech-loading firearms were made in the early 18th century. One such gun known to have belonged to Philip V of Spain, and was manufactured circa 1715, probably in Madrid. It came with a ready-to load reusable cartridge.[7]
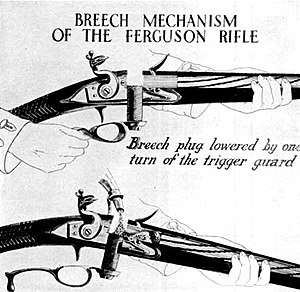
Patrick Ferguson, a British Army officer, developed in 1772 the Ferguson rifle, a breech-loading flintlock firearm. Roughly two hundred of the rifles were manufactured and used in the Battle of Brandywine, during the American Revolutionary War, but shortly after they were retired and replaced with the standard Brown Bess musket.
Later on into the mid-19th century, there were attempts in Europe at an effective breech-loader. There were concentrated attempts at improved cartridges and methods of ignition.
In Paris in 1808, in association with French gunsmith François Prélat, Jean Samuel Pauly created the first fully self-contained cartridges:[8] the cartridges incorporated a copper base with integrated mercury fulminate primer powder (the major innovation of Pauly), a round bullet and either brass or paper casing.[9][10] The cartridge was loaded through the breech and fired with a needle. The needle-activated central-fire breech-loading gun would become a major feature of firearms thereafter.[11] The corresponding firearm was also developed by Pauly.[8] Pauly made an improved version, which was protected by a patent on 29 September 1812.[8]
The Pauly cartridge was further improved by the French gunsmith Casimir Lefaucheux in 1828, by adding a pinfire primer, but Lefaucheux did not register his patent until 1835: a pinfire cartridge containing powder in a card-board shell.
In 1845, another Frenchman Louis-Nicolas Flobert invented, for indoor shooting, the first rimfire metallic cartridge, constituted by a bullet fit in a percussion cap.[12][13] Usually derived in the 6 mm and 9 mm calibres, it is since then called the Flobert cartridge but it does not contain any powder; the only propellant substance contained in the cartridge is the percussion cap itself.[14] In English-speaking countries the Flobert cartridge corresponds to the .22 BB and .22 CB ammunitions.
In 1846, yet another Frenchman, Benjamin Houllier, patented the first fully metallic cartridge containing powder in a metallic shell.[15] Houllier commercialised his weapons in association with the gunsmiths Blanchard or Charles Robert.[16][17] But the subsequent Houllier and Lefaucheux cartridges, even if they were the first full-metal shells, were still pinfire cartridges, like those used in the LeMat (1856) and Lefaucheux (1858) revolvers, although the LeMat also evolved in a revolver using rimfire cartridges.
The first centrefire cartridge was introduced in 1855 by Pottet, with both Berdan and Boxer priming.[18]
In 1842, the Norwegian Armed Forces adopted the breechloading caplock, the Kammerlader, one of the first instances in which a modern army widely adopted a breechloading rifle as its main infantry firearm.
The Dreyse Zündnadelgewehr (Dreyse needle gun) was a single-shot breech-loading rifle using a rotating bolt to seal the breech. It was so called because of its .5-inch needle-like firing pin, which passed through a paper cartridge case to impact a percussion cap at the bullet base. It began development in the 1830s under Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse and eventually an improved version of it was adopted by Prussia in the late 1840s. The paper cartridge and the gun had numerous deficiencies; specifically, serious problems with gas leaking. However, the rifle was used to great success in the Prussian army in the Austro-Prussian war of 1866. This, and the Franco-Prussian war of 1870–71, eventually caused much interest in Europe for breech loaders and the Prussian military system in general.
In 1860, the New Zealand government petitioned the Colonial Office for more soldiers to defend Auckland.[19] The bid was unsuccessful and the government began instead making inquiries to Britain to obtain modern weapons. In 1861 they placed orders for the Calisher and Terry carbine, which used a breech loading system using a bullet consisting of a standard Minié lead bullet in .54 calibre backed by a charge and tallowed wad, wrapped in nitrated paper to keep it waterproof. The carbine had been issued in small numbers to English cavalry (Hussars) from 1857. About 3–4,000 carbines were brought into New Zealand a few years later. The carbine was used extensively by the Forest Rangers, an irregular force led by Gustavus von Tempsky that specialized in bush warfare and reconnaissance. Von Tempsky liked the short carbine, which could be loaded while lying down. The waterproofed cartridge was easier to keep dry in the New Zealand bush. Museums in New Zealand hold a small number of these carbines in good condition.[20][21]
During the American Civil War, at least nineteen types of breech-loaders were fielded.[22] The Sharps used a successful dropping block design. The Greene used rotating bolt-action, and was fed from the breech. The Spencer, which used lever-actuated bolt-action, was fed from a seven-round detachable tube magazine. The Henry and Volcanic used rimfire metallic cartridges fed from a tube magazine under the barrel. These held a significant advantage over muzzle-loaders. The improvements in breech-loaders had spelled the end of muzzle-loaders. To make use of the enormous number of war surplus muzzle-loaders, the Allin conversion Springfield was adopted in 1866. General Burnside invented a breech-loading rifle before the war, the Burnside carbine.
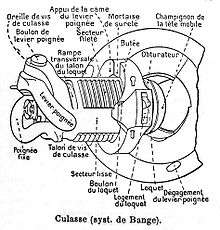
The French adopted the new Chassepot rifle in 1866, which was much improved over the needle gun as it had dramatically fewer gas leaks due to its de Bange sealing system. The British initially took the existing Enfield and fitted it with a Snider breech action (solid block, hinged parallel to the barrel) firing the Boxer cartridge. Following a competitive examination of 104 guns in 1866, the British decided to adopt the Peabody-derived Martini-Henry with trap-door loading in 1871.
.jpg)
Single-shot breech-loaders would be used throughout the latter half of the 19th century, but were slowly replaced by various designs for repeating rifles, first used in the American Civil War. Manual breech-loaders gave way to manual magazine feed and then to self-loading rifles.
Breechloading is still commonly used in shotguns and hunting rifles.
Artillery
The first modern breech-loading rifled gun is a breech-loader invented by Martin von Wahrendorff with a cylindrical breech plug secured by a horizontal wedge in 1837. In the 1850s and 1860s, Whitworth and Armstrong invented improved breech loading artillery.
The M1867 naval guns produced in Imperial Russia[23] at the Obukhov State Plant used Krupp technology.
See also
- Breechblock
- Rifled musket
- Rifled breechloader
References
- W. Greener (2013). Modern Breech-Loaders 1871. Read Books Limited. p. 170. ISBN 978-1-4474-8414-1.
- Ralph P. Gallwey (2013). Swivel-Guns - Breechloaders And Muzzleloaders. Read Books Limited. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-4733-8374-6.
- Held, Robert (1957). The Age of Firearms. A Pictorial History. California: Harper & Row. pp. 20. ISBN 051724666X.
- Tower of London exhibit.
- Zhao Shi-zhen(趙士禎).Shén qì pu (神器譜). 1598.
- Breech-loading arquebuses of the Ming Dynasty, retrieved 11 February 2018
- Musée de l'Armée exhibit, Paris.
- Chemical Analysis of Firearms, Ammunition, and Gunshot Residue by James Smyth Wallace, p. 24
- http://www.sil.si.edu/smithsoniancontributions/HistoryTechnology/pdf_hi/SSHT-0011.pdf.
- Pauly, Roger A.; Pauly, Roger (16 May 2018). "Firearms: The Life Story of a Technology". Greenwood Publishing Group – via Google Books.
- Carman, W. Y. (1 March 2004). "A History of Firearms: From Earliest Times to 1914". Dover Publications – via Google Books.
- History of firearms Archived 2015-12-22 at the Wayback Machine (fireadvantages.com)
- How guns work Archived 2015-12-22 at the Wayback Machine (fireadvantages.com)
- Shooting section (la section de tir) Archived 2013-11-10 at the Wayback Machine of the official website (in French) of a modern indoor shooting association in Belgium, Les Arquebusier de Visé.
- Les Lefaucheux, by Maître Simili, Spring 1990 (in French)
- "An example of a Benjamin Houllier gun manufactured in association with the gunsmith Blanchard". littlegun.info.
- "An example of a Benjamin Houllier gun manufactured in association with the gunsmiths Blanchard and Charles Robert". littlegun.info.
- David Westwood (2005). Rifles: An Illustrated History of Their Impact. ABC-CLIO. p. 29. ISBN 978-1-85109-401-1.
- Belich, James (1986). The New Zealand Wars. Auckland: Penguin. pp. 119–125. ISBN 0-14-027504-5.
- Te Awamutu Museum, Te Awamutu, Waikato, New Zealand. Research notes and a C and T carbine
- "Terry Carbines", Te Papa
- American Breech-loading Small Arms: A Description of Late Inventions, Including the Gatling Gun, and a Chapter on Cartridges, January 1, 1872, p. 14
- The History of Russian Artillery since the mid-19th century up to 1917 Archived July 11, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
Further reading
- Greener, William Wellington. The Breechloader and How to Use It ... Illustrated. London: Cassell & Co, 1892. OCLC 560426421
- Held, Robert. The Age of Firearms; A Pictorial History from the Invention of Gunpower to the Advent of the Modern Breechloader. Northfield, Ill: Gun Digest Co, 1970. ISBN 069580068X OCLC 85426
- Layman, George J. A Guide to the Ballard Breechloader. Union City, TN: Pioneer Press, 1997. OCLC 38968829
External links
- "Breech Loading Rifled Artillery". Global Security. Retrieved 2009-02-25.
- "History of the Rifled Cannon: Discovery of the Breech-Loading Gun and Conical Projectiles". The New York Times. July 12, 1861. Archived from the original on February 8, 2013. Retrieved 2009-02-25.
- "Notes on the History of the Breech-Loading Gun". Scientific American. 70 (22): cover, 343. 2 June 1894.
- Firearms from the collections of the Prince of Liechtenstein, an exhibition catalog from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF), which contains material on breech-loading weapons