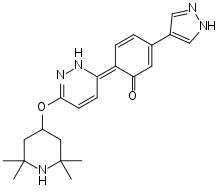
Branaplam
Branaplam (development codes LMI070 and NVS-SM1) is an experimental drug being developed by Novartis to treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). It is a pyridazine derivative that works by increasing the amount of functional survival of motor neuron protein produced by the SMN2 gene through modifying its splicing pattern.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LMI070; NVS-SM1 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H27N5O2 |
| Molar mass | 393.491 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
As of July 2019, branaplam is in a phase-II clinical trial in children with SMA type 1.[3][4][5]
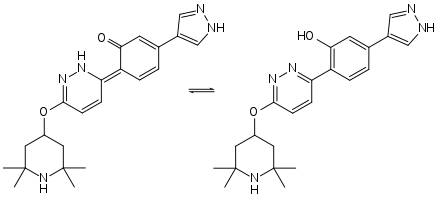
Keto-enol tautomerism of branaplam
References
- Palacino J, Swalley SE, Song C, Cheung AK, Shu L, Zhang X, et al. (July 2015). "SMN2 splice modulators enhance U1-pre-mRNA association and rescue SMA mice". Nature Chemical Biology. 11 (7): 511–7. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1837. PMID 26030728.
- "LMI070". SMA News Today. Retrieved 2017-03-10.
- "An Open Label Study of LMI070 in Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)". ClinicalTrials.gov. Retrieved 2017-03-10.
- "Novartis Releases Update on LMI070 (Branaplam) Clinical Trial". CureSMA. 2017-09-20. Archived from the original on 2017-11-25. Retrieved 2017-10-07.
- "| Novartis announced that enrollment for the ongoing clinical trial of branaplan is now closed". 20 May 2019. Retrieved 2019-07-12.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.