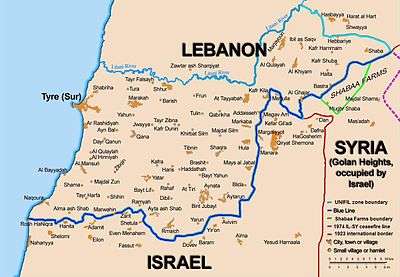
Blue Line (Lebanon)
The Blue Line is a border demarcation between Lebanon and Israel published by the United Nations on 7 June 2000 for the purposes of determining whether Israel had fully withdrawn from Lebanon.
By September 2018 Israel completed 11 kilometers of a concrete barrier along its border with Lebanon designed to protect Israeli communities from Hezbollah infiltrations.[1]
Background
On 11 March 1978 Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) operatives, led by Dalal Mugrabi, carried out the Coastal Road massacre within Israel which resulted in the deaths of 37 Israelis, including 13 children. In response, Israeli forces invaded southern Lebanon from which the PLO operated regularly during the 1970s. Starting on the night of March 14–15 and culminating a few days later, Israel Defense Forces (IDF) troops occupied the entire southern part of the country except for the city of Tyre and its surrounding area. This operation is known in Israel as Operation Litani.
On 15 March 1978 the Lebanese government submitted a strong protest to the United Nations Security Council against the Israeli invasion, stating that it had no connection with the Palestinian operation. On 19 March 1978 the Council adopted Resolution 425, in which it called upon Israel to cease immediately its military action and withdraw its forces from all Lebanese territory. It also established the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL). The first UNIFIL troops arrived in the area on 23 March 1978.
Definition
The Blue Line is based on the deployment of the IDF prior to 14 March 1978. It should not be confused with the Green Line, established in 1949, which is the armistice line of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, nor the Green Line in Beirut during the violence of the 1980s. The 1949 line is in turn the same as the 1923 Mandate Line which was the border between French- and British-mandated territory (see: Paulet–Newcombe Agreement); Lebanon is a former French mandate and Palestine / Israel a former British mandate. (See League of Nations). The 1949 agreement stated that the border would follow the 1923 line.[2] In 1923, 38 boundary markers were placed along the 49 mile border and a detailed text description was published. The 2000 Blue Line differs in about a half dozen short stretches from the 1949 line, though never by more than 475 meters.
Borders are usually negotiated between countries, and between 1950 and 1967 Israeli and Lebanese surveyors managed to complete 25 non-contiguous kilometers and mark (but not sign) another quarter of the international border. On 17 April 2000, when Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak announced that Israel would begin withdrawing its forces from Lebanon, the Lebanese government did not want to take part in marking the border. The UN thus conducted its own survey based on the line discussed in United Nations Security Council Resolution 425.
On 25 May 2000 the government of Israel notified the Secretary-General that Israel had redeployed its forces in compliance with Security Council resolutions 425.
From 24 May to 7 June 2000, the Special Envoy travelled to Israel and Lebanon to follow up on the implementation of the Secretary-General's May 22 report. The United Nations cartographer and his team, assisted by UNIFIL, worked on the ground to identify a line to be adopted for the practical purposes of confirming the Israeli withdrawal. While it was agreed that this would not be a formal border demarcation, the aim was to identify a line on the ground closely conforming to the internationally recognized boundaries of Lebanon, based on the best available cartographic and other documentary evidence.
On 7 June the completed map showing the withdrawal line was formally transmitted by the Force Commander of UNIFIL to his Lebanese and Israeli counterparts. Notwithstanding their reservations about the line, the Governments of Israel and Lebanon confirmed that identifying this line was solely the responsibility of the United Nations and that they would respect the line as identified. On 8 June UNIFIL teams led by Lebanese Brig. General Imad Anka and Brig. General Amin Htait commenced the work of verifying the Israeli withdrawal behind the line.
On 16 June the Secretary-General reported to the Security Council that Israel had withdrawn its forces from Lebanon in accordance with resolution 425 (1978) and met the requirements defined in his report of 22 May 2000; namely, Israel had completed the withdrawal in conformity with the line identified by the United Nations, South Lebanese Army militia had been dismantled, and all detainees held at Al-Khiam prison had been freed.[3]
The withdrawal line has been termed the Blue Line in all official UN communications since.
Violations of the Blue line
2000 Hezbollah cross-border raid
On 7 October 2000 three Israeli soldiers—Adi Avitan 22, Staff Sgt. Benyamin Avraham 21, and Staff Sgt. Omar Sawaid 27—were abducted by Hezbollah forces. They were abducted while patrolling the southern (Israeli) side of the demarcation line recognized by the Secretary-General and the Security Council as the Israeli deployment line[4] The soldiers were killed either during the attack or in its immediate aftermath.[5]
2006 Hezbollah cross-border raid
Hezbollah precipitated the 34-day-long 2006 Lebanon War when its militants fired rockets at Israeli border towns as a diversion for an anti-tank missile attack on two armored Humvees patrolling the Israeli side of the border fence.[6] Of the seven Israeli soldiers in the two jeeps, two were wounded, five were killed, and two soldiers were taken to Lebanon.[6] Israel responded with massive airstrikes and artillery fire on targets in Lebanon and a ground invasion of southern Lebanon.[7]
Israeli violations of Lebanon's airspace
Following 2000 withdrawal, Lebanon's military authorities report Israeli jets have violated the UN resolution 1701 by entering the country's airspace and breaking sound barriers over several villages in southern parts of the nation. Lebanese troops have responded by firing at the Israeli jets with anti-aircraft weapons. Lebanese officials have filed over 1600 air space violations by Israel since the 2000 withdrawal.[8]
2010 Israel–Lebanon border clash
On 3 August 2010 Lebanese Armed Forces soldiers opened fire on Israeli army soldiers performing tree-cutting maintenance work on the Israeli side of the Blue Line as confirmed by UNIFIL.[9] One Israeli was killed by Lebanese army fire and three Lebanese died when the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) responded. Lebanese Information Minister Tarek Mitri stated despite the fact that Lebanon accepted earlier the Blue line "The area where the tree was to be cut yesterday […] is south of the Blue Line but is Lebanese territory." [10] UNIFIL determined that the Israeli troops were on Israeli territory.
2011 Israel–Lebanon border clash
On 1 August 2011, UNIFIL confirmed a border incident in which no one was hurt. Israel and Lebanon offered differing accounts of the incident. A Lebanese military official said Israeli troops crossed the Blue Line 30 meters into Lebanese territory, prompting Lebanese soldiers to fire warning shots and the Israeli troops to retreat and fire at Lebanese border posts. The Israeli military sources said their forces were within Israeli territory when they came under fire from across the border.[11][12]
2013 Hanikra border clash
On 15 December 2013, a Lebanese Army sniper shot dead an Israeli soldier in the Rosh Hanikra border.[13]
2015 Shebaa farms incident
On 28 January 2015, Hezbollah fired an anti-tank missile at an Israeli military convoy in the Shebaa farms, killing two soldiers and wounding seven.[14] In response, Israel fired at least 50 artillery shells across the border into southern Lebanon, in which a Spanish UN peacekeeper was killed.[15]
2018 Operation Northern Shield
On 4 December 2018, Israel initiated Operation Northern Shield to destroy cross-border tunnels built by Hezbollah along Lebanon's border with Israel.[16]
2020 Israel–Hezbollah clashes
On 27 July 2020, there was an exchange of fire between Israeli soldiers and four Hezbollah members.[17][18][19][20]
See also
- Good Fence
- Green Line (Israel)
- Green Line (Lebanon)
- Purple Line
- Shebaa Farms
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1559
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1583
- South Lebanon security belt
References
- "IDF: No Hezbollah militant will return alive from infiltration attempt". Jerusalem Post. 2018-09-06.
- "International Boundary Studies for most of the world". Archived from the original on 2008-09-24. Retrieved 2008-11-24.
- "18 Jun 2000] SC/6878 : SECURITY COUNCIL ENDORSES SECRETARY-GENERAL'S CONCLUSION ON ISRAELI WITHDRAWAL FROM LEBANON AS OF 16 JUNE". Un.org. Retrieved 2011-03-19.
- "Israelis Held by the Hizbullah - Oct 2000-Jan 2004". mfa.gov.il. Archived from the original on 2007-02-10.
- "Israel, Hezbollah swap prisoners". CNN. January 29, 2004. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- The New York Times via the International Herald Tribune (12 July 2006). "Clashes spread to Lebanon as Hezbollah raids Israel". Retrieved 16 August 2007.
- Urquhart, Conal (2006-08-11). "Computerised weaponry and high morale". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2006-10-08.
- "Lebanon to UN: Israel breached truce deal hundreds of times".
- UNIFIL says Israelis were in their territory, Beirut refutes claim
- "UN disputes Lebanese claim Israel violated border". Archived from the original on 2010-08-07. Retrieved August 4, 2010.
- Israeli and Lebanese troops trade fire
- Israel and Lebanon exchange shots on border
- Troops shot on Israel-Lebanon border
- Two Israeli Soldiers Killed in Attack Claimed by Lebanon's Hezbollah
- Two Israeli soldiers killed in Hezbollah missile attack
- "Israel targets Hezbollah 'terror tunnels'". BBC News. 4 December 2018.
- "Lebanon's Hezbollah denies infiltration attempt or clashes near Lebanese frontier". 27 July 2020 – via www.reuters.com.
- "Netanyahu warns Hezbollah against playing with fire after frontier incident". 27 July 2020 – via www.reuters.com.
- "i24NEWS". www.i24news.tv.
- Azhari, Timour. "Lebanon's Hezbollah accuses Israel of fabricating border clash". www.aljazeera.com.
- Lebanon Background, UNIFIL, 2006.
- Ze'ev Schiff, "Thin Blue Line", Ha'aretz, 23 June 2000.
External links
- SECURITY COUNCIL ENDORSES SECRETARY-GENERAL’S CONCLUSION ON ISRAELI WITHDRAWAL FROM LEBANON AS OF 16 JUNE UN Security Council Press Release SC/6878, 16 June 2000