Bjorøy
Bjorøyna or Bjorøy is an island in Øygarden Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. The 4.1-square-kilometre (1.6 sq mi) island is located south of the island of Litlesotra, west of the Bergen Peninsula, north of the island of Tyssøyna, and east of the island of Sotra.
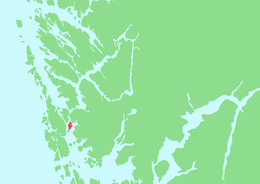 Location of the island | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Vestland, Norway |
| Coordinates | 60.3140°N 5.1742°E |
| Area | 4.1 km2 (1.6 sq mi) |
| Administration | |
Norway | |
| County | Vestland |
| Municipality | Øygarden |
Bjorøy is connected to the mainland city of Bergen by a subsea road tunnel called the Bjorøy Tunnel. It is also connected to the small island of Tyssøy in neighboring Sund municipality by a bridge. Bjorøy has 878 inhabitants (September 2012),[1] and several hundred vacation cabins.[2]
History
Due to its favourable location, proximity to Bergen, and the construction of the tunnel, the island has in recent years been seeing strong population growth.[3] To prevent uncontrolled development, a building ban was instituted in 2007 but was later removed. The ban was instituted after a non-legally binding cap that only allowed ten new houses to be built on the island per year. The purpose was to ensure that the population growth did not surpass the growth of drinking water availability and kindergarten capacity (among other things), but the cap proved to be ineffective.[4][5]
Geography
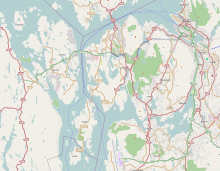
Bjorøy is located in the Raunefjorden between the island of Store Sotra and Bergen. Although Bjorøy is connected only to Bergen by road, the island is part of Øygarden municipality. To get to the rest of the municipality, Bjorøy's residents must drive north into Bergen, then west over a bridge to get back to Øygarden. To the south of Bjorøy is the smaller island of Tyssøy. Tyssøy is connected to Bjorøy by a bridge which is in turn connected to Bergen by a tunnel.
Transport
The subsea tunnel Bjorøytunnelen was opened in 1996, replacing the ferry between the island and Alvøen in Bergen. Plans for a tunnel connecting Bjorøy with Bergen were presented in the late 1980s.[6] By the early 1990s, the island's population had been decreasing for several years, and the sole grocery store on the island closed in 1991.[2] In 1993, the Norwegian government approved the plans for the tunnel, and construction began the same year.[7][8] The construction of the tunnel proved challenging: the bedrock quality was worse than anticipated. Delayed by almost a year, the tunnel finally opened on 7 May 1996.[9]
References
- Hilde Heian (2005). "Nå er det bom slutt!" (in Norwegian). Bergens Tidende. Archived from the original on 2005-03-11. Retrieved 2008-10-30.
- Lindebotten, John (27 February 1993). "Bjorøy ventar på tunnel". Bergens Tidende.
- "Folk flytter fra øyene tross milliarder til bru". NRK. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- Sæverås, Karstein (3 January 2009). "– Bjorøyna tåler meir utbygging". VestNytt.
- Lunde, Einar. "Tiltak i høve til auka utbygging på Bjorøyna - Endring av føresegnene til kommuneplanen" (PDF). Fjell kommune. Retrieved 20 May 2010.
- Bjerkestrand, Frode (17 June 1992). "På jakt etter første Bjorøy-folket". Bergens Tidende.
- Røyrane, Eva (15 May 1993). "Bjorøy vert landfast i 1995". Bergens Tidende.
- Valderhaug, Rune (30 September 1993). "Jubel på Bjorøy for tunnelstart". Bergens Tidende.
- Pettersen, Eivind A. (8 May 1996). "Tunnelfest med bismak". Bergens Tidende.