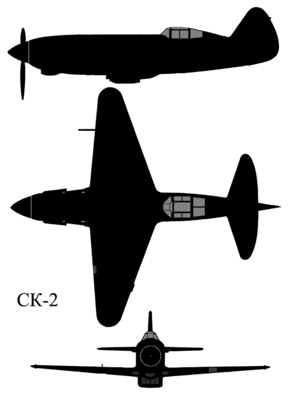
Bisnovat SK-2
The SK-2 (Skorostnii Krylo – high speed wing), was a fighter aircraft designed and built in the USSR from 1940.
| SK-2 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Fighter |
| National origin | USSR |
| Manufacturer | Bisnovat |
| Designer | Matus Bisnovat |
| First flight | October 1940 |
| Number built | 1 |
| Developed from | Bisnovat SK-1 |
Development
After working as an engineer under Tairov at the OKO in Kiev, Bisnovat was permitted to form his own OKB with the task of designing and building a high speed research aircraft, which emerged as the SK-1. The performance and handling of this aircraft prompted authorization for a fighter derivative
Construction of the SK-2 was of light-alloy stressed skin, with single plate web spar wings skinned with light-alloy sheet, smoothed to mirror finish accurate profiles using marquisette fabric, cork dust, open weave and adhesive as filler. Initially the wing was of NACA 23014.5 profile with slotted Vlasov style flaps, and fabric covered ailerons. The tail-unit also had fabric covered control surfaces, and trim tabs, with all controls 100% mass balanced.
The M-105 engine was fitted in a low drag installation with a pressurised coolant system which required a radiator of only 0.17m^2 frontal area (approx ½ that of a similar unpressurised coolant system), hydraulically retractable main and tail undercarriages with fully closing doors also reduced drag.
The SK-2 was a minimum change fighter derivative of the SK-1 with a normal protruding enclosed cockpit, normal light alloy wing skinning, enlarged fin and rudder, and two 12.7mm BS machine-guns in the top decking of the forward fuselage. Flown in October 1940 by G.M. Shiyanov, but no production was authorised.
Specifications (SK-2)
Data from Gunston, Bill. "Encyclopaedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995". London:Osprey. 1995. ISBN 1-85532-405-9
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 8.28 m (27 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 7.3 m (23 ft 11.5 in)
- Wing area: 9.57 m2 (103 sq ft)
- Airfoil: max speed
- Empty weight: 1,850 kg (4,078 lb)
- Gross weight: 2,300 kg (5,071 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Klimov M-105 (VK-105) , 783 kW (1,050 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 660 km/h (413 mph, 359 kn)
- Endurance: 45 minutes
- Rate of climb: 19.23 m/s (3,785.6 ft/min)
Armament
- 2 × 12.7mm BS machine guns in a pivoting tray above the engine.
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
Related lists
References
- Gunston, Bill. “The Osprey Encyclopaedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995”. London, Osprey. 1995. ISBN 1-85532-405-9