Bis(chloroethyl) ether
Bis(chloroethyl) ether is an organic compound with the formula O(CH2CH2Cl)2. It is an ether with two 2-chloroethyl substituents. It is a colorless liquid with the odor of a chlorinated solvent.[3]
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Chloro-2-(2-chloroethoxy)ethane | |
| Other names
Oxygen mustard; Bis(2-chloroethyl) ether; 2,2'-Dichlorodiethyl ether; Chlorex; Khloreks; DCEE; 2-Chloroethyl ether; 1,1'-oxybis[2-chloroethane] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.519 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1916 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8Cl2O | |
| Molar mass | 143.01 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear liquid[1] |
| Odor | Chlorinated, solvent-like[1] |
| Density | 1.22 g/mL[1] |
| Melting point | −50 °C; −58 °F; 223 K [1] |
| Boiling point | 178 °C; 352 °F; 451 K decomposes |
| 10,200 mg/L | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.7 mmHg (20 °C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Very toxic (T+) Dangerous for the environment (N) Vesicant |
| GHS pictograms |     |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H226, H300, H310, H315, H319, H330, H351 |
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P284, P301+310, P302+350, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P310, P320 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 55 °C; 131 °F; 328 K |
| Explosive limits | 2.7%-?[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration) |
77 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 152 ppm (mouse, 2 hr) 500 ppm (guinea pig, 1 hr)[2] |
LCLo (lowest published) |
250 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 500 ppm (guinea pig, 5 hr)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 15 ppm (90 mg/m3) [skin][1] |
REL (Recommended) |
Ca TWA 5 ppm (30 mg/m3) ST 10 ppm (60 mg/m3) [skin][1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
Ca [100 ppm][1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
sulfur mustard nitrogen mustard |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Reactions and applications
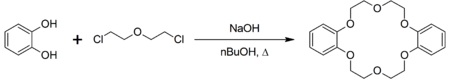
Bis(chloroethyl) ether is less reactive than the corresponding sulfur mustard S(CH2CH2Cl)2.[3] In the presence of base, it reacts with catechol to form dibenzo-18-crown-6:[4]
Bis(chloroethyl) ether can be used in the synthesis of the cough suppressant fedrilate. It is combined with benzyl cyanide and two molar equivalents of sodamide in a ring-forming reaction. When treated with strong base, it gives divinyl ether, an anesthetic:[5]
- O(CH2CH2Cl)2 + 2 KOH → O(CH=CH2)2 + 2 KCl + 2 H2O
Toxicity
The LD50 is 74 mg/kg (oral, rat).[3] Bis(chloroethyl) ether is considered as a potential carcinogen.[6]
gollark: I'm probably going to try to trade for balloons or something.
gollark: Now to trade for... I don't know, stuff.
gollark: Thanks!
gollark: Wait, WHAT?!
gollark: Yes, go.
See also
- Bis(chloromethyl) ether
- Sulfur mustard
References
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0196". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Dichloroethyl ether". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Wang, Q. Q.; Begum, R. A.; Day, V. W.; Bowman-James, K. (2012). "Sulfur, Oxygen, and Nitrogen Mustards: Stability and Reactivity Wang, Qi-Qiang; Begum, Rowshan Ara; Day, Victor W.; Bowman-James, Kristin". Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. 10 (44): 8786–8793. doi:10.1039/c2ob26482j. PMID 23070251. S2CID 9721325.
- Pedersen, C. J. (1972). "Macrocyclic Polyethers: Dibenzo-18-Crown-6 Polyether and Dicyclohexyl-18-Crown-6 Polyether". Organic Syntheses. 52: 66.; Collective Volume, 6, p. 395
- Wollweber, Hartmund (2000). "Anesthetics, General". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_289.
- "CDC - Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH): Dichloroethyl ether - NIOSH Publications and Products". www.cdc.gov. 2017-11-07. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.