Big Lost River
The Big Lost River is a major river in the U.S. state of Idaho, about 135 miles (217 km) long.[5]
| Big Lost River | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
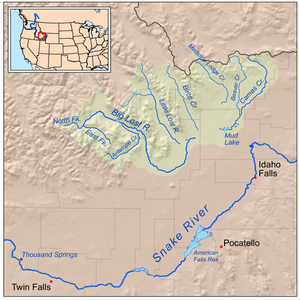 Map of the lost streams of Idaho including the Big Lost River | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Idaho |
| Cities | Mackay, Arco, Atomic City |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Confluence of North Fork and East Fork Big Lost River |
| • location | Custer County, Idaho |
| • coordinates | 43°56′01″N 114°06′38″W[1] |
| • elevation | 6,860 ft (2,090 m) |
| Mouth | Big Lost River Sinks |
• location | Butte County, Idaho |
• coordinates | 43°47′39″N 112°50′26″W |
• elevation | 4,790 ft (1,460 m) |
| Length | 135 mi (217 km) |
| Basin size | 1,867 sq mi (4,840 km2)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | near Arco[3] |
| • average | 86.3 cu ft/s (2.44 m3/s)[4] |
| • minimum | 0 cu ft/s (0 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 2,500 cu ft/s (71 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | North Fork Big Lost River, Thousand Springs Creek |
| • right | East Fork Big Lost River, Antelope Creek |
Description
The river starts in the Rocky Mountains and flows in a generally southeast direction into the Snake River Plain. True to its name, the Big Lost River's surface flow does not reach any larger river, but vanishes into the Snake River Aquifer at the Big Lost River Sinks, giving the river its name.[2] The river is one of the Lost streams of Idaho, several streams that flow into the plain and disappear into the ground.
It rises at the confluence of the North Fork and East Fork Big Lost River deep in the Pioneer Mountains, a subrange of the Rockies, in Custer County, south-central Idaho. It flows northeast then turns sharply southeast at the confluence with Thousand Springs Creek which comes in from the left and into Butte County. The river is dammed to form Mackay Reservoir near the town of Mackay, then continues south through an agricultural valley, passing Arco. After Arco the river begins flowing east, then northeast, and finally due north. The river terminates at the Big Lost River Sinks, a patch of marshland where its water drains into the ground.
Despite the fact that its surface flow is lost (hence its name) a short distance out of the mountains, the river is hydrologically connected to the Snake River, the largest river of Idaho by discharge, via the Snake River Aquifer and various springs along the course of the Snake in its journey through the plain.
References
- "Big Lost River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. 1979-06-21. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- "Subbasin Assessment – Watershed Characterization" (PDF). Big Lost River Subbasin Assessment and TMDL. Idaho Department of Environmental Quality. 2004-05-06. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 November 2010. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- "USGS Gage #13132500 on the Big Lost River near Arco, ID" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 1946-present. Retrieved 2010-11-21. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - "USGS Gage #13132500 on the Big Lost River near Arco, ID" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 1946-present. Retrieved 2010-11-21. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map Archived 2012-04-05 at WebCite, accessed May 4, 2011
External links
![]()