Bicinchoninic acid
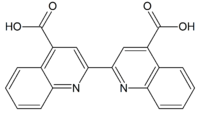
Bicinchoninic acid /baɪsɪnkɔːnɪnɪk/ is a weak acid composed of two carboxylated quinoline rings.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[2,2'-Biquinoline]-4,4'-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Bicinchoninic acid 4,4'-Dicarboxy-2,2'-biquinoline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.628 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H12N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 344.326 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Cream colored powder |
| Odor | Characteristic odor |
| Melting point | 365 to 367 °C (689 to 693 °F; 638 to 640 K) |
| Partially soluble in cold water, hot water | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Will irritate eyes and mucous membranes. |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bicinchoninic acid is most commonly employed by biochemists in the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay, which is used to determine the total level of protein in a solution. In this assay, two molecules of bicinchoninic acid chelate a single Cu+ ion, forming a purple water-soluble complex that strongly absorbs light at 562 nm.[1]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
