Benzoyl chloride
Benzoyl chloride, also known as benzenecarbonyl chloride, is an organochlorine compound with the formula C6H5COCl. It is a colourless, fuming liquid with an irritating odour. It is mainly useful for the production of peroxides but is generally useful in other areas such as in the preparation of dyes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and resins.
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzoyl chloride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.464 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1736 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5ClO | |||
| Molar mass | 140.57 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Benzaldehyde like but more pungent | ||
| Density | 1.21 g/mL, liquid | ||
| Melting point | −1 °C (30 °F; 272 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 197.2 °C (387.0 °F; 470.3 K) | ||
| reacts | |||
| -75.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | Fisher Scientific MSDS | ||
| GHS pictograms | 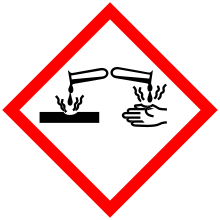  | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H302, H312, H314, H317, H332 | ||
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P333+313, P363, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 72 °C (162 °F; 345 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
benzoic acid, benzoic anhydride, benzaldehyde | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Preparation
Benzoyl chloride is produced from benzotrichloride using either water or benzoic acid:[1]
- C6H5CCl3 + H2O → C6H5COCl + 2 HCl
- C6H5CCl3 + C6H5CO2H → 2 C6H5COCl + HCl
As with other acyl chlorides, it can be generated from the parent acid and other chlorinating agents phosphorus pentachloride or thionyl chloride. It was first prepared by treatment of benzaldehyde with chlorine.[2]
An early method for production of benzoyl chloride involved chlorination of benzyl alcohol.[3]
Reactions
It reacts with water to produce hydrochloric acid and benzoic acid:
- C6H5COCl + H2O → C6H5CO2H + HCl
Benzoyl chloride is a typical acyl chloride. It reacts with alcohols to give the corresponding esters. Similarly, it reacts with amines to give the amide.[4][5]
It undergoes the Friedel-Crafts acylation with aromatic compounds to give the corresponding benzophenones and related derivatives.[6] With carbanions, it serves again as a source of "PhCO+".[7]
Benzoyl peroxide, a common reagent in polymer chemistry, is produced industrially by treating benzoyl chloride with hydrogen peroxide and sodium hydroxide:[8]
- 2 C6H5COCl + H2O2 + 2 NaOH → (C6H5CO)2O2 + 2 NaCl + 2 H2O
References
- Maki, Takao; Takeda, Kazuo (2000). "Benzoic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_555.
- Friedrich Wöhler, Justus von Liebig (1832). "Untersuchungen über das Radikal der Benzoesäure". Annalen der Pharmacie. 3 (3): 262–266. doi:10.1002/jlac.18320030302. hdl:2027/hvd.hxdg3f.
- US1851832, 29 March 1932
- Marvel, C. S.; Lazier, W. A. (1929). "Benzoyl Piperidine". Organic Syntheses. 9: 16. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.009.0016.
- Prasenjit Saha, Md Ashif Ali, and Tharmalingam Punniyamurthy "Ligand-free Copper(ii) Oxide Nanoparticles Catalyzed Synthesis Of Substituted Benzoxazoles" Org. Synth. 2011, volume 88, pp. 398. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.088.0398. (an illustrative reaction of an amine with benzoyl chloride).
- Minnis, Wesley (1932). "Phenyl Thienyl Ketone". Organic Syntheses. 12: 62. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.012.0062.
- Fujita, M.; Hiyama, T. (1990). "Directed Reduction of a beta-keto Amide: Erythro-1-(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-phenylpropanoyl)piperidine". Organic Syntheses. 69: 44. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.069.0044.
- El-Samragy, Yehia (2004). "Chemical and Technical Assessment". Benzoyl Peroxide (PDF). 61st JECFA (Technical report). Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. p. 1. Retrieved 31 October 2013.