Bacillus flexus
Bacillus flexus is an aerobic, Gram-variable, rod-shaped, endospore-forming, oxidase positive bacteria. The endospores are ellipsoidal, located in central/paracentral, unswollen sporangia. In laboratory conditions, it produces opaque, creamish, raised margin colonies at 30 ± 2°C when incubated at 24–72 hrs. on Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA). These bacteria may be isolated from feces (poultry) and soil.
| Bacillus flexus | |
|---|---|
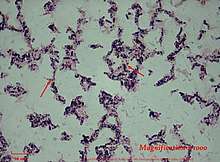 | |
| Bacillus flexus gram stain under 1000 magnification | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | Bacillus flexus |
Human pathogenicity has not been well described at this time.[1][2]
References
- Zhao, Jian; Lan, Xiaojun; Su, Jun; Sun, Lei; Rahman, Erkin (June 2008). "Isolation and identification of an alkaliphilic Bacillus flexus XJU-3 and analysis of its alkaline amylase". Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao = Acta Microbiologica Sinica. 48 (6): 750–756. ISSN 0001-6209. PMID 18720839.
- Jebeli, Mohammad Ahmadi; Maleki, Afshin; Amoozegar, Mohammad Ali; Kalantar, Enayatollah; Izanloo, Hassan; Gharibi, Fardin (2017-02-01). "Bacillus flexus strain As-12, a new arsenic transformer bacterium isolated from contaminated water resources". Chemosphere. 169: 636–641. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.129. ISSN 0045-6535. PMID 27912188.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.