BOGESTRA
The Bochum-Gelsenkirchener Straßenbahnen AG (English: Bochum-Gelsenkirchen Streetcars Corporation), abbreviated BOGESTRA, is a public transport operator in the Ruhr area, most notably in the cities of Bochum, Gelsenkirchen and Herne. As of 2012, the company operated, in whole or in part, 9 rail lines[1] (2 Stadtbahn, and 7 tram), and 65 bus lines.[1] In 2012, BOGESTRA transported a total of 144.9 million passengers.[1] The company is a member of the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr (VRR) public transport association.
 | |
| Founded | 13 January 1896 |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Universitätsstraße 58 44789 Bochum |
| Locale | Bochum, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany |
| Service area | Bochum, Gelsenkirchen, Herne and Witten |
| Alliance | Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr (VRR) |
| Routes | Multi-Modal regional transit network consisting of: |
| Stops | 1,285 (total)[1] |
| Fleet | 381 vehicles total:
|
| Annual ridership | 144.9 million (2012)[1] |
| Website | BOGESTRA AG |
History
BOGESTRA was founded by the cities of Bochum and Gelsenkirchen and Siemens & Halske AG in Berlin on 13 January 1896. At the time of the founding of the company, the transit network consisted of three lines built by Siemens & Halske in 1894 and 1895. Thus, BOGESTRA already had, at the time of its founding, approximately 15.1 kilometres (9.4 mi) of streetcar network. The construction and operation of these lines remained with the Siemens & Halske AG, while BOGESTRA itself initially took only functional control. In the next 10 years the network grew rapidly.
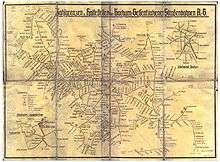
Much of the streetcar network was damaged or destroyed by Allied bombing during World War II. On 24 May 1945, the deployment of transit personnel and the operation of approximately 55 kilometres (34 mi) of the rail network were resumed. In the period following the war, additional routes and lines were repaired and reopened. By the end of 1950, a total of 27 lines were back in operation, and the reconstruction of the rail system could be considered complete.
In contrast to the meter-gauge streetcar lines that BOGESTRA had operated since the 1890s, the 1970s and 1980s saw the planning for Stadtbahn lines throughout the Rhine-Ruhr region, including in the BOGESTRA operating area. BOGESTRA's new Stadbahn line would be operated on standard gauge rail with high platform stations in its own right-of-way using Stadtbahn B train cars. The first Stadtbahn section was opened on 2 September 1989 between Bochum Central Station and Castle Herne Strünkede as Line U35. This was also the first inter-city subway tunnel in Germany, because the city boundary between Bochum and Herne is crossed underground on Line U35. According to BOGESTRA, the underground section connecting these cities is still unique in Germany. An extension of Line U35 south from the Bochum Central Station to the Ruhr-University Bochum and on to Hustadt took place on 28 November 1993.
Current service
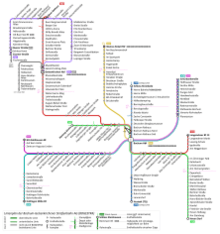
Stadtbahn
BOGESTRA currently exclusively operates Line U35, which is integrated in the Rhine-Ruhr Stadtbahn network. The U35 route runs between Herne and Bochum, serving 21 stations (15 of which are underground, with 6 being above-ground).[2]
Line U35 opened on 2 September 1989, then operating a route between Castle Herne Strünkede and Bochum Central Station. An extension of the line from the Bochum Central Station south to the Ruhr-University Bochum and to Hustadt opened for service on 28 November 1993. Planned sections of the U35 line northwest to Recklinghausen and southeast to Witten were never implemented due to the associated costs to these respective municipalities.
| Line | Route | Stations[2] (underground) |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| U35 | Schloss Strünkede – Herne Bahnhof – Bochum-Riemke – Bochum Hauptbahnhof – Ruhr-Universität – Bochum-Querenburg, Hustadt | 21 (15) |
Operated exclusively by BOGESTRA. |
In addition, a second Stadtbahn line operates in the BOGESTRA region: one of the Essen Stadtbahn routes (operated by Ruhrbahn), Line U11, operates partially in the BOGESTRA transit area though only for its northernmost 3 stations.[2]
| Line | Route | Stations (underground) |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| U11 | Buerer Str. (in Gelsenkirchen) – E-Karnap – Altenessen – Berliner Platz – Essen Hbf – Rüttenscheid – Essen Messe/Gruga | 23 (13) |
Operated by Ruhrbahn. Only 3 stations in BOGESTRA area. |
Tram
The tram system dates back to the 1890s. As of 2012, BOGESTRA exclusively operates the following six tram lines:[2]
| Line | Route | Stations[2] (underground) |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 301 | Gelsenkirchen Hbf – Bismarck – Buer – Horst | 34 (7) |
|
| 302 | Gelsenkirchen-Buer Rathaus – Gelsenkirchen Hbf – Bochum Hbf – Laer Mitte - Langendreer S | 44 (7) |
|
| 306 | Wanne-Eickel Hbf – Bochum Hbf | 21 (1) |
Also operates as a Night Express. |
| 308 | Bochum-Gerthe Schürbankstraße – Bochum Hbf – Weitmar – Linden – Hattingen Mitte | 38 (4) |
|
| 310 | Bochum-Höntrop Kirche – Bochum Hbf – Witten Rathaus – Heven Dorf | 39 (4) |
|
| 318 | Bochum-Gerthe Schürbankstraße – Bochum Hbf – Weitmar – Linden – Dahlhausen Bf. | 32 (4) |
Also operates as a Night Express. |
In addition, a seventh tram line also operates in the BOGESTRA region: an Essen tram route, Line 107, operates partially in the BOGESTRA transit area though only for its northernmost 11 stations.[2]
| Line | Route | Stations | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 107 | Gelsenkirchen Hbf – Feldmark – Trabrennbahn – Essen-Katernberg – Zeche Zollverein – Essen Hbf – Bredeney |
34 | Operated by Ruhrbahn. Only 11 stations in BOGESTRA area. On Saturday mornings, only operates to Trabrennbahn. |
Bus
As of 2012, BOGESTRA operates 65 bus lines.[1] BOGESTRA bus lines are generally given route numbers in the 300s (like the tram route numbers).
See also
- Rhein-Ruhr Stadtbahn
- Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr (VRR)
- Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn
- List of rapid transit systems
References
- "Das Unternehmen auf einen Blick - Zahlen und Fakten" [The Enterprise at a Glance - Facts and Figures] (in German). BOGESTRA AG. 2013. Retrieved 2013-10-25.
- "BOGESTRA-Schienennetz" [BOGESTRA-Rail Network Plan] (PDF) (in German). BOGESTRA AG. June 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-11-01. Retrieved 2013-10-25.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bogestra. |
- Official website

- Ruhrbahn – official site (in German)
- Documents and clippings about BOGESTRA in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW