Anoxomer
Anoxomer is a food additive with E number E323. It is a non-digestible polymeric antioxidant.[1] It was designed to allow the introduction of established antioxidants in a non-absorbable manner in order to avoid potential health risk associated with their digestion.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Poly Ao-79 | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| E number | E323 (antioxidants, ...) |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| variable | |
| Molar mass | variable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
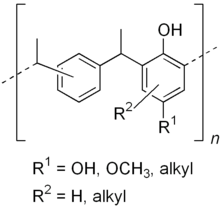
Anoxomer is prepared by condensation polymerization of divinylbenzene and a mixture of antioxidant monomers including tert-butylhydroquinone, tert-butylphenol, hydroxyanisole, p-cresol and 4,4'-isopropylidenediphenol.[2][3]
References
- Weinshenker, Ned M (1980). "Anoxomer. A new nonabsorbable antioxidant". Food Technology. 34 (11): 40–49.
- Thomas E. Furia, CRC Handbook of Food Additives, Volume II, 1980, ISBN 978-0-8493-0543-6
- Code of Federal Regulations Archived October 13, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, Title 21, Volume 3, April 1, 2006 (21CFR172.105)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.