Ammonium azide
Ammonium azide is the chemical compound with the formula NH4N3, being the salt of ammonia and hydrazoic acid. Like other inorganic azides, this colourless crystalline salt is a powerful explosive, although it has a remarkably low sensitivity. NH4N3 is physiologically active and inhalation of small amounts causes headaches and palpitations. It was first obtained by Theodor Curtius in 1890, along with other azides.
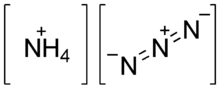 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Ammonium trinitride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.093 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NH4N3, NH3.HN3 | |
| Molar mass | 60.059 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.3459 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) |
| Boiling point | 400 °C (752 °F; 673 K) (decomposes) |
| Structure[1] | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Pman | |
a = 8.930, b = 8.642, c = 3.800 | |
Formula units (Z) |
4 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Very toxic, explosive |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Ammonium nitrate Ammonium cyanide |
Other cations |
Sodium azide Potassium azide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure
Ammonium azide is ionic. Ammonium azide contains about 93% nitrogen by weight as ammonium cation and azide anion. It is a structural isomer of tetrazene.
gollark: Really?
gollark: Your board would need BIÖS updates for 3rd gen.
gollark: More RAM would be nice, but I think the current thing only takes ECC.
gollark: I think most of the power consumption from the server is just various inefficiencies from it being old and not prioritized for efficiency.
gollark: The idea of switching to a newer platform is so that the power consumption will be lower and so I can switch to passive cooling.
References
- Frevel, Ludo K. (1 January 1936). "The Crystal Structure of Ammonium Azide, NH4N3". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials. 94 (1–6): 197. doi:10.1524/zkri.1936.94.1.197.
- Yakovleva, G. S.; Kurbangalina, R. Kh.; Stesik, L. N. (1977). "Detonation properties of ammonium azide". Combustion, Explosion, and Shock Waves. 13 (3): 405. doi:10.1007/BF00740326.
- Salim de Amorim, Helio; do Amaral, M. R.; Pattison P.; Ludka I. P.; Mendes, J. C. (2002). "Ammonium azide: A Commented Example of an Ab Initio Structure (Re-)Determination From X-Ray Diffraction" (PDF). Revista de la Sociedad Quimica de México. 45 (4): 313–319. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-04-06.
- Curtius, Th. (1890). "Ueber Stickstoffwasserstoffsäure (Azoimid) N3H". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 23 (2): 3023–3033. doi:10.1002/cber.189002302232.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.