alpha-Propiolactone
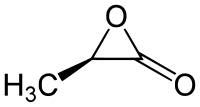
α-Propiolactone, or 2-methyl-α-lactone, is a chemical compound of the lactone family, with a three-membered ring. It is a stable product which can be obtained from the 2-bromo-propionate anion.[1] It is an intermediate in the decomposition of 2-chloropropionic acid in the gas phase.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-methyloxiran-2-one | |
| Other names
α-Propiolactone 2-methyl-α-lactone | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEMBL | |
PubChem CID |
|
| Properties | |
| C3H4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 72.06 g mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- The Chemical Thesaurus, (2R)-2-Methyl alpha-lactone data page. Accessed on 2009-10-07.
- Vicent S. Safont, Vicente Moliner, Juan Andrés, Luís R. Domingo (1997), Theoretical Study of the Elimination Kinetics of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives in the Gas Phase. Decomposition of 2-Chloropropionic Acid. J. Physical Chemistry series A, volume 101, issue 10, pp. 1859–1865. doi:10.1021/jp962533t
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.