Allolactose
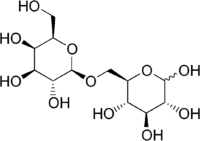
Allolactose is a disaccharide similar to lactose. It consists of the monosaccharides D-galactose and D-glucose linked through a β1-6 glycosidic linkage instead of the β1-4 linkage of lactose. It may arise from the occasional transglycosylation of lactose by β-galactosidase.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-[[(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol | |
| Other names
6-O-β-D-Galactopyranosyl-D-glucose; β-D-Galactopyranosyl (1→6)-D-glucose | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.296 g/mol |
| Density | 1.768 g/mL |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is an inducer of the lac operon in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. It binds to a subunit of the tetrameric lac repressor, which results in conformational changes and reduces the binding affinity of the lac repressor to the lac operator, thereby dissociating it from the lac operator. The absence of the repressor allows the transcription of the lac operon to proceed. A non-hydrolyzable analog of allolactose, isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), is normally used in molecular biology to induce the lac operon.
External links
- allolactose at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Illustration of function