Alaninol
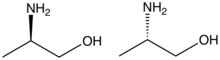
Alaninol is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(NH2)CH2OH. A colorless solid, the compound is classified as an amino alcohol. It can be generated by converting the carboxylic group of alanine to an alcohol with a strong reducing agent such as lithium aluminium hydride,[1]. The compound is chiral, and as is normal for chiral compounds, the physical propertiies of the racemate differ somewhat from those of the enantiomers. It is a precursor to numerous chiral ligands used in asymmetric catalysis.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Aminopropan-1-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.535 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H9NO | |
| Molar mass | 75.111 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Melting point | 96 °C racemate 72-72 °C for R or S |
| Boiling point | 174.5 °C (346.1 °F; 447.6 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 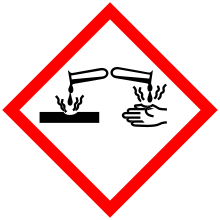 |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H314 |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Dickman, D.A.; Meyers, A.I.; Smith, G.A.; Gawley, R.E. (1990). "Reduction of α-Amino Acids". Organic Syntheses. 7: 530. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.063.0136. Archived from the original on 15 January 2011. Retrieved 11 October 2012.
- Dawson, Graham J.; Frost, Christopher G.; Williams, Jonathan M.J.; Coote, Steven J. (1993). "Asymmetric palladium catalysed allylic substitution using phosphorus containing oxazoline ligands". Tetrahedron Letters. 34 (19): 3149–3150. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)93403-8.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.