Airs above the ground
The airs above the ground or school jumps are a series of higher-level, Haute ecole, classical dressage movements in which the horse leaves the ground. They include the capriole, the courbette, the mezair, the croupade and the levade. None are typically seen in modern competitive dressage. They are performed by horses of various riding academies such as the Spanish Riding School in Vienna and the Cadre Noir in Saumur, and may be seen in other dressage performances. The levade and courbette are a particular feature of the Doma Menorquina, the riding tradition of the island of Menorca.[1] Horses such as the Andalusian, Lusitano, Lipizzan and Menorquín are the breeds most often trained to perform the airs today, in part due to their powerfully conformed hindquarters, which allow them the strength to perform these difficult movements. There were originally seven airs, many of which were used to build into the movements performed today.





There is a popular conception that these movements were originally taught to horses for military purposes, and indeed both the Spanish Riding School and the Cadre Noir are military foundations. However, while agility was necessary on the battlefield, most of the airs as performed today would have exposed the vulnerable underbelly of the horse to the weapons of foot soldiers.[2] It is therefore more likely that the airs were exercises to develop the military horse and rider, rather than to be employed in combat.
Horses are usually taught each air on the long rein without a rider, which is less strenuous for the animal. However, each movement is meant to eventually be performed under a rider.
The pesade and the levade
The pesade and levade are the first airs taught to the High School horse, and it is from these that all other airs are taught. In the pesade, the horse raises its forehand off the ground and tucks the forelegs evenly, carrying all weight on the hindquarters, to form a 45 degree angle with the ground.
The levade was first taught at the beginning of the 20th century, asking the horse to hold a position approximately 30–35 degrees from the ground. Unlike the pesade, which is more of a test of balance, the decreased angle makes the levade an extremely strenuous position to hold, and requires a greater effort from the horse. Therefore, many horses are not capable of a good-quality levade. The levade is also a transition movement between work on the ground and the airs above the ground. Neither of these movements are equivalent to rearing, as they require precise control, excellent balance, and a great deal of strength, and are the product of correct training, rather than resistance from the horse.
The horse is asked to enter the pesade or levade from the piaffe, which asks the horse to increasingly engage its hindquarters, lowering them toward the ground and bringing the hind legs more toward its center of gravity. This gives the viewer the impression that the horse appears to sink down in back and rise in front. The position is held for a number of seconds, and then the horse quietly puts the forelegs back on the ground and proceeds at the walk, or stands at the halt. The levade is considered to be pinnacle of collection, as the horse carries all weight on the back legs, and has an extreme tucking of the hindquarters and coiling of the loins.
The capriole, the croupade and the ballotade
In the capriole (meaning leap of a goat), the horse jumps from a raised position of the forehand straight up into the air, kicks out with the hind legs, and lands more or less on all four legs at the same time. It requires an enormously powerful horse to perform correctly, and is considered the most difficult of all the airs above the ground. It is first introduced with the croupade, in which the horse does not kick out at the height of elevation, but keeps the hind legs tucked tightly under, and remains parallel to the ground. The horse is then taught the ballotade. In this movement, the horse's hind hooves are positioned so one can see its shoes if watching from behind, but the horse is not asked to kick out. When the horse demonstrates proficiency in the ballotade, the capriole is introduced.
The courbette
In the courbette, the horse raises its forehand off the ground, tucks up forelegs evenly, and then jumps forward, never allowing the forelegs to touch down, in a series of "hops". Extremely strong and talented horses can perform five or more leaps forward before having to touch down with the forelegs, although it is more usual to see a series of three or four leaps. The courbette, like the capriole, is first introduced through the easier croupade.
The mezair
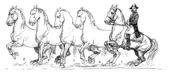
In the mezair, the horse rears up and strikes out with its forelegs. It is similar to a series of levades with a forward motion (not in place), with the horse gradually bringing its legs further under himself in each successive movement and lightly touching the ground with the front legs before pushing up again. The mezair was originally called the courbette by the old dressage masters. It is no longer practiced at the Spanish Riding School.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Airs above the ground. |
References
- "Menorca – Insel der Pferde" (PDF). Equus (in German). 2011 (2). April–June 2011. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
Menorca – Island of horses
- Chamberlin, J. Edward. Horse: How the Horse Has Shaped Civilizations. Bluebridge, 2006, pp. 166–67 ISBN 0-9742405-9-1