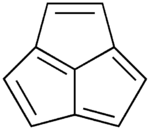
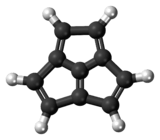
Acepentalene
Acepentalene is a tricyclic anti-aromatic compound. Its molecular formula is C10H6. It consists of three five-membered rings fused across three of the five carbon atoms. The central carbon atom in acepentalene is part of all three rings. There are formally five double bonds in acepentalene, so that the molecule formally contains four double bonds on the exterior, and one double bond from the central carbon to the exterior of the ring system.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cyclopenta[cd]pentalene | |
| Other names
Acepentylene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H6 | |
| Molar mass | 126.158 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The acepentalene dianion, which can be stabilized by two lithium atoms, is more stable. The radical anion is also known.[1]
References
- Armin de Meijere; Fabian Gerson; Peter R. Schreiner; Pascal Merstetter; Franz-Manfred Schüngel (1999). "The radical anion of acepentalene". Chem. Commun.: 2189–2190. doi:10.1039/a906972k.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.