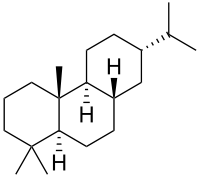
Abietane
Abietane is a diterpene that forms the structural basis for a variety of natural chemical compounds such as abietic acid,[1] carnosic acid, and ferruginol which are collectively known as abietanes or abietane diterpenes.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
13α-Isopropylpodocarpane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H36 | |
| Molar mass | 276.508 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.876 g/ml |
| Melting point | 338 °C (640 °F; 611 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- San Feliciano, Arturo; Gordaliza, Marina; Salinero, Miguel A.; Miguel del Corral, Jose M (1993). "Abietane acids: sources, biological activities, and therapeutic uses". Planta Medica. 59 (6): 485–490. doi:10.1055/s-2006-959744. PMID 8302943.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.